Omics Profiling of S2P Mutant Fibroblasts as a Mean to Unravel the Pathomechanism and Molecular Signatures of X-Linked MBTPS2 Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- PMID: 34093655
- PMCID: PMC8176293
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.662751
Omics Profiling of S2P Mutant Fibroblasts as a Mean to Unravel the Pathomechanism and Molecular Signatures of X-Linked MBTPS2 Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Abstract
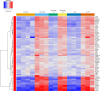
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is an inherited skeletal dysplasia characterized by low bone density, bone fragility and recurrent fractures. The characterization of its heterogeneous genetic basis has allowed the identification of novel players in bone development. In 2016, we described the first X-linked recessive form of OI caused by hemizygous MBTPS2 missense variants resulting in moderate to severe phenotypes. MBTPS2 encodes site-2 protease (S2P), which activates transcription factors involved in bone (OASIS) and cartilage development (BBF2H7), ER stress response (ATF6) and lipid metabolism (SREBP) via regulated intramembrane proteolysis. In times of ER stress or sterol deficiency, the aforementioned transcription factors are sequentially cleaved by site-1 protease (S1P) and S2P. Their N-terminal fragments shuttle to the nucleus to activate gene transcription. Intriguingly, missense mutations at other positions of MBTPS2 cause the dermatological spectrum condition Ichthyosis Follicularis, Atrichia and Photophobia (IFAP) and Keratosis Follicularis Spinulosa Decalvans (KFSD) without clinical overlap with OI despite the proximity of some of the pathogenic variants. To understand how single amino acid substitutions in S2P can lead to non-overlapping phenotypes, we aimed to compare the molecular features of MBTPS2-OI and MBTPS2-IFAP/KFSD, with the ultimate goal to unravel the pathomechanisms underlying MBTPS2-OI. RNA-sequencing-based transcriptome profiling of primary skin fibroblasts from healthy controls (n = 4), MBTPS2-OI (n = 3), and MBTPS2-IFAP/KFSD (n = 2) patients was performed to identify genes that are differentially expressed in MBTPS2-OI and MBTPS2-IFAP/KFSD individuals compared to controls. We observed that SREBP-dependent genes are more downregulated in OI than in IFAP/KFSD. This is coupled to alterations in the relative abundance of fatty acids in MBTPS2-OI fibroblasts in vitro, while no consistent alterations in the sterol profile were observed. Few OASIS-dependent genes are suppressed in MBTPS2-OI, while BBF2H7- and ATF6-dependent genes are comparable between OI and IFAP/KFSD patients and control fibroblasts. Importantly, we identified genes involved in cartilage physiology that are differentially expressed in MBTPS2-OI but not in MBTPS2-IFAP/KFSD fibroblasts. In conclusion, our data provide clues to how pathogenic MBTPS2 mutations cause skeletal deformities via altered fatty acid metabolism or cartilage development that may affect bone development, mineralization and endochondral ossification.
Keywords: MBTPS2; X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta; connective tissue; site 2 protease; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2021 Lim, Marfurt, Lindert, Opitz, Ndarugendamwo, Srikanthan, Poms, Hersberger, Langhans, Haas, Rohrbach and Giunta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Perturbations in fatty acid metabolism and collagen production infer pathogenicity of a novel MBTPS2 variant in Osteogenesis imperfecta.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 25;14:1195704. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1195704. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37305034 Free PMC article.
-
MBTPS2, a membrane bound protease, underlying several distinct skin and bone disorders.J Transl Med. 2021 Mar 20;19(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02779-5. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33743732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ichthyosis follicularis, atrichia, and photophobia syndrome associated with a new mutation in MBTPS2.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015 Jul;40(5):529-32. doi: 10.1111/ced.12587. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25683132
-
Recurrent splice-site mutation in MBTPS2 underlying IFAP syndrome with Olmsted syndrome-like features in a Chinese patient.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014 Mar;39(2):158-61. doi: 10.1111/ced.12248. Epub 2013 Dec 7. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24313295
-
Novel MBTPS2 missense mutation causes a keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans phenotype: mutation update and review of the literature.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016 Oct;41(7):757-60. doi: 10.1111/ced.12889. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27663151 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Landscape of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approaches.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jan 2;7(1):72-96. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00324. eCollection 2024 Jan 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38230285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perturbations in fatty acid metabolism and collagen production infer pathogenicity of a novel MBTPS2 variant in Osteogenesis imperfecta.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 25;14:1195704. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1195704. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37305034 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the Genetics of Osteogenesis Imperfecta.Calcif Tissue Int. 2024 Dec;115(6):891-914. doi: 10.1007/s00223-024-01266-5. Epub 2024 Aug 11. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024. PMID: 39127989 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

