Transcriptome-Wide Identification of G-to-A RNA Editing in Chronic Social Defeat Stress Mouse Models
- PMID: 34093668
- PMCID: PMC8173075
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.680548
Transcriptome-Wide Identification of G-to-A RNA Editing in Chronic Social Defeat Stress Mouse Models
Abstract
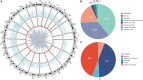
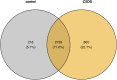
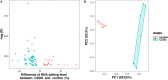
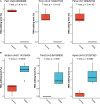
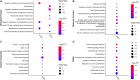
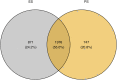
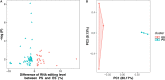
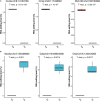
Emerging evidence suggests that RNA editing is associated with stress, neurological diseases, and psychiatric disorders. However, the role of G-to-A RNA editing in chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) remains unclear. We herein identified G-to-A RNA editing and its changes in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a key region of the brain reward system, in CSDS mouse models under emotional stress (ES) and physiological stress (PS) conditions. Our results revealed 3812 high-confidence G-to-A editing events. Among them, 56 events were significantly downregulated while 23 significantly upregulated in CSDS compared to controls. Moreover, divergent editing patterns were observed between CSDS mice under ES and PS conditions, with 42 and 21 events significantly upregulated in PS and ES, respectively. Interestingly, differential RNA editing was enriched in genes with multiple editing events. Genes differentially edited in CSDS included those genetically associated with mental or neurodevelopmental disorders, especially mood disorders, such as FAT atypical cadherin 1 and solute carrier family 6 member 1. Notably, changes of G-to-A RNA editing were also implicated in ionotropic glutamate receptors, a group of well-known targets of adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing. Such results demonstrate dynamic G-to-A RNA editing changes in the brain of CSDS mouse models, underlining its role as a potential molecular mechanism of CSDS and stress-related diseases.
Keywords: RNA editing; depression; emotional stress; physical stress; post-traumatic stress disorder; social defeat; ventral tegmental area.
Copyright © 2021 Tao, Ren, Wei, Zhang, Xu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA Editing Within Corticolimbic Brain Regions Is Regulated in Response to Chronic Social Defeat Stress in Mice.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Apr 26;10:277. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00277. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31133890 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of chronic physical and emotional social defeat stress effects on mesocorticolimbic circuit activation and voluntary consumption of morphine.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 16;7(1):8445. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09106-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28814751 Free PMC article.
-
[Altered Expression of Neurotransmitters Systems' Genes in the Ventral Tegmental Area of Depressive Male Mice: Data of RNA-Seq].Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2017 Jan;67(1):113-128. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2017. PMID: 30695556 Russian.
-
Essential Role of Mesolimbic Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Social Stress-Induced Depressive Behaviors.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Sep 15;80(6):469-478. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26858215 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological sequelae of witnessing stressful events in adult mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Jan 1;73(1):7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.06.006. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 22795644 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Brain Epitranscriptomic Analysis Revealed Altered A-to-I RNA Editing in Septic Patients.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 26;13:887001. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.887001. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35559016 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated Winning and Losing Experiences in Chronic Social Conflicts Are Linked to RNA Editing Pattern Difference.Front Psychiatry. 2022 May 19;13:896794. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.896794. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35664469 Free PMC article.
-
Epitranscriptomic investigation of myopia-associated RNA editing in the retina.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 28;17:1220114. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1220114. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37449273 Free PMC article.
-
Viral N protein hijacks deaminase-containing RNA granules to enhance SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis.EMBO J. 2024 Dec;43(24):6444-6468. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00314-y. Epub 2024 Nov 20. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39567830 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing in response to COVID-19 vaccines: unveiling dynamic epigenetic regulation of host immunity.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 6;15:1413704. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1413704. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39308856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blair I. P., Chetcuti A. F., Badenhop R. F., Scimone A., Moses M. J., Adams L. J., et al. (2006). Positional cloning, association analysis and expression studies provide convergent evidence that the cadherin gene FAT contains a bipolar disorder susceptibility allele. Mol. Psychiatry 11 372–383. 10.1038/sj.mp.4001784 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

