Ranking Biomarkers of Aging by Citation Profiling and Effort Scoring
- PMID: 34093670
- PMCID: PMC8176216
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.686320
Ranking Biomarkers of Aging by Citation Profiling and Effort Scoring
Abstract
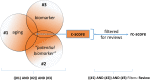
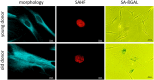
Aging affects most living organisms and includes the processes that reduce health and survival. The chronological and the biological age of individuals can differ remarkably, and there is a lack of reliable biomarkers to monitor the consequences of aging. In this review we give an overview of commonly mentioned and frequently used potential aging-related biomarkers. We were interested in biomarkers of aging in general and in biomarkers related to cellular senescence in particular. To answer the question whether a biological feature is relevant as a potential biomarker of aging or senescence in the scientific community we used the PICO strategy known from evidence-based medicine. We introduced two scoring systems, aimed at reflecting biomarker relevance and measurement effort, which can be used to support study designs in both clinical and research settings.
Keywords: aging; biomarker; health; senescence; survival.
Copyright © 2021 Hartmann, Hartmann, Secci, Hermann, Fuellen and Walter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

