METTL3-Mediated m6A Methylation Regulates Muscle Stem Cells and Muscle Regeneration by Notch Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 34093712
- PMCID: PMC8140833
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9955691
METTL3-Mediated m6A Methylation Regulates Muscle Stem Cells and Muscle Regeneration by Notch Signaling Pathway
Abstract
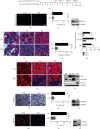
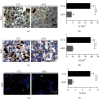
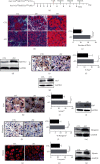
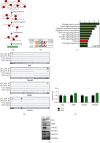
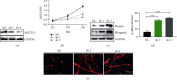
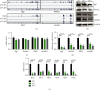
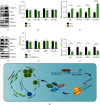
The Pax7+ muscle stem cells (MuSCs) are essential for skeletal muscle homeostasis and muscle regeneration upon injury, while the molecular mechanisms underlying muscle stem cell fate determination and muscle regeneration are still not fully understood. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification is catalyzed by METTL3 and plays important functions in posttranscriptional gene expression regulation and various biological processes. Here, we generated muscle stem cell-specific METTL3 conditional knockout mouse model and revealed that METTL3 knockout in muscle stem cells significantly inhibits the proliferation of muscle stem cells and blocks the muscle regeneration after injury. Moreover, knockin of METTL3 in muscle stem cells promotes the muscle stem cell proliferation and muscle regeneration in vivo. Mechanistically, METTL3-m6A-YTHDF1 axis regulates the mRNA translation of Notch signaling pathway. Our data demonstrated the important in vivo physiological function of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in muscle stem cells and muscle regeneration, providing molecular basis for the therapy of stem cell-related muscle diseases.
Copyright © 2021 Yu Liang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
METTL3-mediated m6A mRNA modification promotes esophageal cancer initiation and progression via Notch signaling pathway.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Jul 21;26:333-346. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.07.007. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34513313 Free PMC article.
-
Mettl3-mediated m6A modification of Fgf16 restricts cardiomyocyte proliferation during heart regeneration.Elife. 2022 Nov 18;11:e77014. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77014. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36399125 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic m6A mRNA Methylation Reveals the Role of METTL3/14-m6A-MNK2-ERK Signaling Axis in Skeletal Muscle Differentiation and Regeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 1;9:744171. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.744171. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34660602 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 plays multiple functions in biological processes.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 1;10(6):1631-1646. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32642280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Role of RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Bone Biology and Osteoporosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jan 10;10:911. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00911. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 31998240 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory role of RNA N6-methyladenosine modifications during skeletal muscle development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 5;10:929183. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.929183. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35990615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Study of mRNAs and lncRNAs Modified by m6A RNA Methylation in the Longissimus Dorsi Muscle Development of Cattle-Yak.Cells. 2022 Nov 17;11(22):3654. doi: 10.3390/cells11223654. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429081 Free PMC article.
-
METTL16 inhibits differentiation and promotes proliferation and slow myofibers formation in chicken myoblasts.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104384. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104384. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39418792 Free PMC article.
-
Current Thoughts of Notch's Role in Myoblast Regulation and Muscle-Associated Disease.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 29;18(23):12558. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182312558. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34886282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering m6A dynamics at a single-base level during planarian anterior-posterior axis specification.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Sep 18;21:4567-4579. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.09.018. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37790241 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

