Deep insight: Convolutional neural network and its applications for COVID-19 prognosis
- PMID: 34093724
- PMCID: PMC8162826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102814
Deep insight: Convolutional neural network and its applications for COVID-19 prognosis
Abstract
Background and objective: SARS-CoV-2, a novel strain of coronavirus' also called coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), a highly contagious pathogenic respiratory viral infection emerged in December 2019 in Wuhan, a city in China's Hubei province without an obvious cause. Very rapidly it spread across the globe (over 200 countries and territories) and finally on 11 March 2020 World Health Organisation characterized it as a "pandemic". Although it has low mortality of around 3% as of 18 May 2021 it has already infected 164,316,270 humans with 3,406,027 unfortunate deaths. Undoubtedly the world was rocked by the COVID-19 pandemic, but researchers rose to all manner of challenges to tackle this pandemic by adopting the shreds of evidence of ML and AI in previous epidemics to develop novel models, methods, and strategies. We aim to provide a deeper insight into the convolutional neural network which is the most notable and extensively adopted technique on radiographic visual imagery to help expert medical practitioners and researchers to design and finetune their state-of-the-art models for their applicability in the arena of COVID-19.
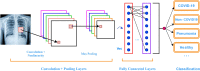
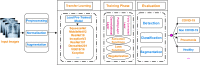
Method: In this study, a deep convolutional neural network, its layers, activation and loss functions, regularization techniques, tools, methods, variants, and recent developments were explored to find its applications for COVID-19 prognosis. The pipeline of a general architecture for COVID-19 prognosis has also been proposed.
Result: This paper highlights recent studies of deep CNN and its applications for better prognosis, detection, classification, and screening of COVID-19 to help researchers and expert medical community in multiple directions. It also addresses a few challenges, limitations, and outlooks while using such methods for COVID-19 prognosis.
Conclusion: The recent and ongoing developments in AI, MI, and deep learning (Deep CNN) has shown promising results and significantly improved performance metrics for screening, prediction, detection, classification, forecasting, medication, treatment, contact tracing, etc. to curtail the manual intervention in medical practice. However, the research community of medical experts is yet to recognize and label the benchmark of the deep learning framework for effective detection of COVID-19 positive cases from radiology imagery.
Keywords: Applications; COVID-19; Challenges; Convolutional neural network; Pandemic.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Applications of machine learning and artificial intelligence for Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic: A review.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020 Oct;139:110059. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110059. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020. PMID: 32834612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Nov;196:105581. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105581. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32534344 Free PMC article.
-
CoroDet: A deep learning based classification for COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021 Jan;142:110495. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110495. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021. PMID: 33250589 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning-based framework for detecting COVID-19 patients using chest X-rays.Multimed Syst. 2022;28(4):1495-1513. doi: 10.1007/s00530-022-00917-7. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Multimed Syst. 2022. PMID: 35341212 Free PMC article.
-
Convolutional neural networks for the diagnosis and prognosis of the coronavirus disease pandemic.Vis Comput Ind Biomed Art. 2021 May 5;4(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s42492-021-00078-w. Vis Comput Ind Biomed Art. 2021. PMID: 33950399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Potential of Big Data Analytics in Urban Epidemiology Control: A Comprehensive Study Using CiteSpace.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 22;20(5):3930. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20053930. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36900941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioelectronic Therapeutics: A Revolutionary Medical Practice in Health Care.Bioelectricity. 2025 Mar 18;7(1):2-28. doi: 10.1089/bioe.2024.0039. eCollection 2025 Mar. Bioelectricity. 2025. PMID: 40342937 Review.
-
A Survey on Deep Learning in COVID-19 Diagnosis.J Imaging. 2022 Dec 20;9(1):1. doi: 10.3390/jimaging9010001. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36662099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence for segmentation and classification of lobar, lobular, and interstitial pneumonia using case-specific CT information.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):579-591. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-945. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38223078 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic detection of multiple types of pneumonia: Open dataset and a multi-scale attention network.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022 Mar;73:103415. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103415. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022. PMID: 34909050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borji A. Negative results in computer vision: a perspective. Image Vis. Comput. 2018;69:1–8.
-
- Guo Y., Liu Y., Oerlemans A., Lao S., Wu S., Lew M.S. Deep learning for visual understanding: a review. Neurocomputing. 2016;187:27–48.
-
- 2019. World Health Organization Updates: Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19) – Events as They Happen.http://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as...
-
- Rustam F., Reshi A.A., Mehmood A., Ullah S., On B., Aslam W., Choi G.S. Covid-19 future forecasting using supervised machine learning models. IEEE Access. 2020
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
