Treatment expectations as a possible prognostic factor for DMARD response in rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 34093746
- PMCID: PMC8142018
- DOI: 10.1177/1759720X211015829
Treatment expectations as a possible prognostic factor for DMARD response in rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The prediction of the individual's response to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is challenging and often limited. Here we evaluated the influence of patients' expectations towards a change in treatment with DMARD on clinical outcome in RA.
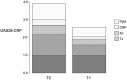
Methods: One hundred patients (74 female) with RA (2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria) and an upcoming change in DMARD treatment due to non-response or adverse effects were included. Patients' treatment beliefs, health-related quality of life and treatment expectations were measured using the Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire (BMQ), the Short Form 36, and self-designed questions about expectations before treatment initiation (T0), and DAS28-CRP was calculated at T0 and after 4 months (T4). Associations between patients' beliefs and expectations and changes in DAS28-CRP (T0 to T4, ΔDAS28-CRP) were explored by regression analyses after multiple imputation.
Results: A total of 99 patients were included, of whom 84 completed all questionnaires. Thirty-six percent of all variability in treatment response (ΔDAS28-CRP) was explained by expectations assessed with the questionnaires and the C-reactive protein (CRP)-value at T0. Among these, the expected improvement rate, with 10.5%, as well as the CRP-value at T0, with 10.6%, had the greatest positive effect whereas the fear of adverse effects, with 11.4%, and the BMQ.concern scale, with 9.0%, had the greatest negative impact on ΔDAS28.
Conclusion: Patients' expectations towards newly induced DMARD therapies influence clinical response and may serve as possible explanatory factors for treatment response affecting subjective and objective outcome parameters.
Clinical trial registration number: DRKS00017005.
Keywords: DMARDs; behavior; biomarkers; patient attitude to health; quality of life; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author(s), 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Disease-modifying treatment for inflammatory rheumatism in sub-Saharan Africa: outcome at 6 months of 205 Senegalese patients with rheumatoid arthritis].Med Sante Trop. 2012 Oct-Dec;22(4):385-9. doi: 10.1684/mst.2012.0096. Med Sante Trop. 2012. PMID: 23352953 French.
-
Real World Experience of Disease Activity in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Response to Treatment With Varios Biologic DMARDs.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 20;9:1303. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01303. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30524277 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-quantitative analysis of 18F fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the assessment of disease activity and therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis: An institutional experience.World J Nucl Med. 2020 Jun 27;19(4):347-352. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_12_20. eCollection 2020 Oct-Dec. World J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 33623503 Free PMC article.
-
The rheumatoid arthritis patient in the clinic: comparing more than 1,300 consecutive DMARD courses.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002 Dec;41(12):1367-74. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.12.1367. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002. PMID: 12468815
-
Meta-Regression of a Dose-Response Relationship of Methotrexate in Mono- and Combination Therapy in Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug-Naive Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017 Oct;69(10):1473-1483. doi: 10.1002/acr.23164. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 27992656 Review.
Cited by
-
Sarcoidosis: Updates on therapeutic drug trials and novel treatment approaches.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 12;9:991783. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.991783. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36314034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaltsonoudis E, Pelechas E, Voulgari PV, et al.. Unmet needs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. An observational study and a real-life experience from a single university center. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2019; 48: 597–602. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JJ, Wells G, Verhoeven AC, et al.. Factors predicting response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: the importance of disease duration. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 22–29. - PubMed
-
- Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Silman AJ, et al.. Predictors of response to anti-TNF-alpha therapy among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006; 45: 1558–1565. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

