MicroRNA expression profiling involved in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity using high-throughput deep-sequencing analysis
- PMID: 34093775
- PMCID: PMC8170198
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2021.12821
MicroRNA expression profiling involved in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity using high-throughput deep-sequencing analysis
Abstract
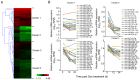
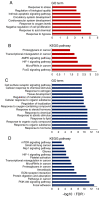
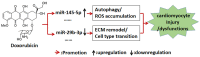
MicroRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) are sensitive biomarkers and endogenous repressors of gene expression by decreasing mRNA stability and interfering with mRNA translation. Despite a number of investigations revealing the dysregulation of miRNA expression associated with cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin (Dox), perturbation of miRNAs directly resulting from Dox at early stage in cardiomyocytes and the target gene interaction remain largely unknown. In the present study, high-throughput deep-sequencing was used to analyze changes in global miRNA expression in H9c2 cardiomyocytes exposed to 5 µg/ml Dox for 0, 12 or 24 h. Compared with the 0-h time point, the expression levels of 386 unique miRNAs were altered. Based on miRNA expression and fold-change, the target genes of 76 selected miRNAs were further analyzed using gene interaction networks and pathway enrichment analysis. These miRNAs were involved in the regulation of different pathways, whose functions included apoptosis, cell proliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, oxidative stress and lipid metabolism. These differentially expressed miRNAs included let-7 family, miR-29b-3p, miR-378-3/5p, miR-351-3p, miR-664-3p, miR-455-3p, miR-298-3p, miR-702-5p, miR-128-1-5p, miR-671 and miR-421-5p. The present data indicated that global wide miRNA profiling in Dox-induced cardiomyocytes may provide a novel mechanistic insight into understanding Dox-induced heart failure and cardiotoxicity, as well as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: cardiomyocyte; cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin; microRNA.
Copyright: © Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MiR-15b-5p is Involved in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Bmpr1a Signal in H9c2 Cardiomyocyte.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2019 Jun;19(3):264-275. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9495-6. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30535663
-
MicroRNAs as early toxicity signatures of doxorubicin in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.Arch Toxicol. 2016 Dec;90(12):3087-3098. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1668-0. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Arch Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26842497 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of let-7f-2-3p by long noncoding RNA NEAT1 inhibits XPO1-mediated HAX-1 nuclear export in both in vitro and in vivo rodent models of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Nov;93(11):3261-3276. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02586-4. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31570982
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13335. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413335. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of microRNA expression profiling studies in heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2021 Jul;26(4):997-1021. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-10071-9. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Heart Fail Rev. 2021. PMID: 33443726 Review.
Cited by
-
Sclerostin is involved in osteogenic transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells in chronic kidney disease-associated vascular calcification with non-canonical Wnt signaling.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):1426-1442. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2114370. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 36017689 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA Expression Profiles in Isolated Ventricular Cardiomyocytes: Insights into Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 12;25(10):5272. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105272. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791311 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑378: An important player in cardiovascular diseases (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2023 Sep;28(3):172. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13059. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37503766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network for Exploring Doxorubicin- and Myocet-Induced Cardiotoxicity in a Translational Porcine Model.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 27;13(12):1711. doi: 10.3390/biom13121711. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136582 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of biomarkers for doxorubicin‑induced cardiac injury in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Oct 5;24(6):712. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11648. eCollection 2022 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36349063 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
