The Overexpression of NMHC IIA Promoted Invasion and Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 34093822
- PMCID: PMC8176418
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.47506
The Overexpression of NMHC IIA Promoted Invasion and Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
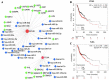
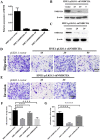
Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a kind of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) with a strong tendency for metastasis and recurrence. Non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIA (NMHC IIA) plays important roles in recurrence and metastasis of cancers. However, the function and mechanism of NMHC IIA expression in NPC remain unclear. Methods: A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed for 141 specimens of HNSCC tissues and 44 control samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Co-expressed genes with MYH9 were identified using LinkedOmics. Transcription factors (TFs) and miRNA regulation network were constructed using Networkanalyst. The migration and invasion ability of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells were evaluated by in vitro migration and matrigel invasion assays, respectively. Results: The public microarray results showed that MYH9 expression levels were upregulated in HNSCC tissues compared with the matched adjacent normal tissues in this study (p<0.0001). The AUC of MYH9 reached up to 0.8303 at a cutoff value of 175.2, with a sensitivity and specificity of 70.21% and 86.36%, respectively. MYH9 expression was increased in lymph node metastasis HNSCC tumors compared with that in tumors without lymph node metastasis (p<0.05) and showed a strong positive association with expression of FLNA. High MYH9 and FLNA expression were related with poorer overall survival in HNSCC. MYH9 with positively associated genes regulated focal adhesion, cell-substrate junction assembly and cell morphogenesis were involved in differentiation using GO and KEGG analysis. MYH9 was correlated with a network of TFs including SP1, SRF, JUN and FOS in HNSCC. The suppression of endogenous NMHC IIA decreased cellular migration and invasion in HNE1 cells and reduced the expression of phosphorylation of EGFR, AKT and ERK. The over-expression of NMHC IIA increased cellular migration and invasion in COS-7 cells and increased the expression of phosphorylation of EGFR, AKT and ERK. Conclusion: Expression of NMHC IIA mRNA was higher in HNSCC than in the adjacent normal tissues. NMHC IIA expression was increased in lymph node metastasis HNSCC tumors compared with tumors without lymph node metastasis. High MYH9 was association with poorer overall survival in HNSCC. NMHC IIA expression increased the invasion and metastasis abilities of the nasopharyngeal cancer cell line in vitro by augmenting the expression of phosphorylation of EGFR, AKT and ERK. These findings will be beneficial for providing an effectively therapeutic strategy for NPC.
Keywords: NMHC IIA; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; invasion; metastasis; nasopharyngeal cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MYH9-siRNA and MYH9 mutant alleles: expression in cultured cell lines and their effects upon cell structure and function.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008 May;65(5):393-405. doi: 10.1002/cm.20268. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008. PMID: 18330899
-
LINC00958 and HOXC13-AS as key candidate biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis.PeerJ. 2020 Feb 13;8:e8557. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8557. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32095369 Free PMC article.
-
Non-muscle myosin II is an independent predictor of overall survival for cystectomy candidates with early-stage bladder cancer.Oncol Rep. 2012 Nov;28(5):1625-32. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1965. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22895805
-
Calprotectin and the Initiation and Progression of Head and Neck Cancer.J Dent Res. 2018 Jun;97(6):674-682. doi: 10.1177/0022034518756330. Epub 2018 Feb 14. J Dent Res. 2018. PMID: 29443623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the nexus between MYH9 and tumors: novel insights and new therapeutic opportunities.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 1;12:1421763. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1421763. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39149512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosome and lipid metabolism-related genes in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a prognosis analysis.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Oct 18;15(20):11331-11368. doi: 10.18632/aging.205130. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37857015 Free PMC article.
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates mitochondrial homeostasis in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Oct 10;14(10):663. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06195-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37816709 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling pathogenesis, biomarkers and potential therapeutic agents for endometriosis associated with disulfidptosis based on bioinformatics analysis, machine learning and experiment validation.J Biol Eng. 2024 Jul 26;18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13036-024-00437-0. J Biol Eng. 2024. PMID: 39061076 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of DGKA indicates poor overall survival of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 17;16(1):1354. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03110-0. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40676285 Free PMC article.
-
Talin2 binds to non-muscle myosin IIa and regulates cell attachment and fibronectin secretion.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 30;14(1):20175. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70866-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39215026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lo KW, Huang DP. Genetic and epigenetic changes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2002;12:451–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

