Coronary microvascular injury in myocardial infarction: perception and knowledge for mitochondrial quality control
- PMID: 34093852
- PMCID: PMC8171103
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.60143
Coronary microvascular injury in myocardial infarction: perception and knowledge for mitochondrial quality control
Abstract
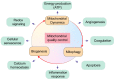
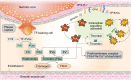
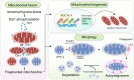
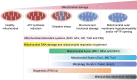
Endothelial cells (ECs) constitute the innermost layer in all blood vessels to maintain the structural integrity and microcirculation function for coronary microvasculature. Impaired endothelial function is demonstrated in various cardiovascular diseases including myocardial infarction (MI), which is featured by reduced myocardial blood flow as a result of epicardial coronary obstruction, thrombogenesis, and inflammation. In this context, understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms governing the function of coronary ECs is essential for the early diagnosis and optimal treatment of MI. Although ECs contain relatively fewer mitochondria compared with cardiomyocytes, they function as key sensors of environmental and cellular stress, in the regulation of EC viability, structural integrity and function. Mitochondrial quality control (MQC) machineries respond to a broad array of stress stimuli to regulate fission, fusion, mitophagy and biogenesis in mitochondria. Impaired MQC is a cardinal feature of EC injury and dysfunction. Hence, medications modulating MQC mechanisms are considered as promising novel therapeutic options in MI. Here in this review, we provide updated insights into the key role of MQC mechanisms in coronary ECs and microvascular dysfunction in MI. We also discussed the option of MQC as a novel therapeutic target to delay, reverse or repair coronary microvascular damage in MI. Contemporary available MQC-targeted therapies with potential clinical benefits to alleviate coronary microvascular injury during MI are also summarized.
Keywords: ECs; coronary microvasculature; mitochondrial quality control; myocardial infarction.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Bassenge E, Heusch G. Endothelial and neuro-humoral control of coronary blood flow in health and disease. Reviews of physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology. 1990;116:77–165. - PubMed
-
- Heusch G. Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17:773–89. - PubMed
-
- Bausch D, Fritz S, Bolm L, Wellner UF, Fernandez-Del-Castillo C, Warshaw AL. et al. Hedgehog signaling promotes angiogenesis directly and indirectly in pancreatic cancer. Angiogenesis. 2020;23:479–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

