Cancer-derived exosomal miR-138-5p modulates polarization of tumor-associated macrophages through inhibition of KDM6B
- PMID: 34093857
- PMCID: PMC8171095
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.51864
Cancer-derived exosomal miR-138-5p modulates polarization of tumor-associated macrophages through inhibition of KDM6B
Abstract
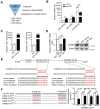
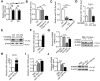
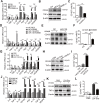
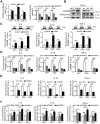
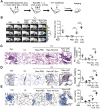
Rationale: Differential activation of macrophages correlates closely with tumor progression, and the epigenetic factor lysine demethylase 6B (KDM6B, previously named JMJD3) mediates the regulation of macrophage polarization through an unknown mechanism. Methods: We developed a suspension coculture system comprising breast cancer cells and macrophages and used RT-qPCR and western blotting to measure KDM6B expression. Bioinformatics and luciferase reporter assays were used to identify candidate microRNAs of cancer cells responsible for the downregulation of KDM6B. To determine if exosomes mediated the transfer of miR-138-5p between cancer cells to macrophages, we treated macrophages with exosomes collected from the conditioned medium of cancer cells. The effects of exosomal miR-138-5p on macrophage polarization were measured using RT-qPCR, flow cytometry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. We employed a mouse model of breast cancer, metastatic to the lung, to evaluate the effects on tumor metastasis of macrophages treated with miR-138-5p-enriched exosomes. To develop a diagnostic evaluation index, the levels of exosomal miR-138-5p in samples from patients with breast cancer were compared to those of controls. Results: Coculture of breast cancer cells led to downregulation of KDM6B expression in macrophages. Cancer cell-derived exosomal miR-138-5p inhibited M1 polarization and promoted M2 polarization through inhibition of KDM6B expression in macrophages. Macrophages treated with exosomal miR-138-5p promoted lung metastasis, and the level of circulating exosomal miR-138-5p positively correlated with the progression of breast cancer. Conclusion: Our data suggest that miR-138-5p was delivered from breast cancer cells to tumor-associated macrophages via exosomes to downregulate KDM6B expression, inhibit M1 polarization, and stimulate M2 polarization. Therefore, exosomal miR-138-5p represents a promising prognostic marker and target for the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: exosomes; lysine demethylase 6B (KDM6B); macrophage polarization; microRNA-138-5p; tumor-associated macrophages.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
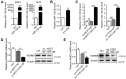
Similar articles
-
Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-191-5p Activates M2-Subtype Macrophages Through SOCS3 to Facilitate Breast Cancer.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 May;66(5):1314-1325. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-01034-0. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38270757
-
Exosomal miR-106a-5p from highly metastatic colorectal cancer cells drives liver metastasis by inducing macrophage M2 polarization in the tumor microenvironment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 9;43(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03204-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39385295 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of exosomal miR-let-7e-5p induces macrophage M2 polarization by targeting Rictor/AKT1 signal pathway in brucellosis patients.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 9;30(1):607. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02867-y. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40635062 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Multifaceted Regulators of Breast Tumor Growth.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 18;22(12):6526. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126526. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-associated macrophages derived exosomes; from pathogenesis to therapeutic opportunities.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Jul 30;136:112406. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112406. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38850795 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-191-5p Activates M2-Subtype Macrophages Through SOCS3 to Facilitate Breast Cancer.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 May;66(5):1314-1325. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-01034-0. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38270757
-
Global Trends and Prospects Regarding Exosomes in Cancer Immunology Research Over the Past 10 Years.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231199892. doi: 10.1177/15330338231199892. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37990510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Exosome-Related Gene Risk Model to Evaluate the Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Predict Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 1;12:736030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.736030. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34659224 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Associated Macrophage in Breast Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 21;26(13):5973. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135973. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation through the mmu_circ_0000349/mmu-miR-138-5p/Jumonji domain-containing protein-3 axis.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 6;9(11):e21885. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21885. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38045146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dehne N, Mora J, Namgaladze D, Weigert A, Brune B. Cancer cell and macrophage cross-talk in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017;35:12–9. - PubMed
-
- Choi J, Gyamfi J, Jang H, Koo JS. The role of tumor-associated macrophage in breast cancer biology. Histol and histopathol. 2018;33:133–45. - PubMed
-
- Tariq M, Zhang J, Liang G, Ding L, He Q, Yang B. Macrophage Polarization: Anti-Cancer Strategies to Target Tumor-Associated Macrophage in Breast Cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118:2484–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

