Pharmacological inhibition of noncanonical EED-EZH2 signaling overcomes chemoresistance in prostate cancer
- PMID: 34093859
- PMCID: PMC8171087
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.49235
Pharmacological inhibition of noncanonical EED-EZH2 signaling overcomes chemoresistance in prostate cancer
Abstract
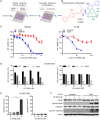
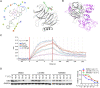
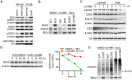
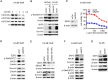
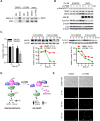
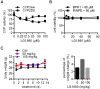
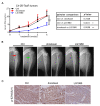
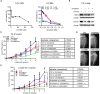
Rationale: Chemoresistance is a major obstacle in prostate cancer (PCa) treatment. We sought to understand the underlying mechanism of PCa chemoresistance and discover new treatments to overcome docetaxel resistance. Methods: We developed a novel phenotypic screening platform for the discovery of specific inhibitors of chemoresistant PCa cells. The mechanism of action of the lead compound was investigated using computational, molecular and cellular approaches. The in vivo toxicity and efficacy of the lead compound were evaluated in clinically-relevant animal models. Results: We identified LG1980 as a lead compound that demonstrates high selectivity and potency against chemoresistant PCa cells. Mechanistically, LG1980 binds embryonic ectoderm development (EED), disrupts the interaction between EED and enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), thereby inducing the protein degradation of EZH2 and inhibiting the phosphorylation and activity of EZH2. Consequently, LG1980 targets a survival signaling cascade consisting of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3), S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2), ATP binding cassette B 1 (ABCB1) and survivin. As a lead compound, LG1980 is well tolerated in mice and effectively suppresses the in vivo growth of chemoresistant PCa and synergistically enhances the efficacy of docetaxel in xenograft models. Conclusions: These results indicate that pharmacological inhibition of EED-EZH2 interaction is a novel strategy for the treatment of chemoresistant PCa. LG1980 and its analogues have the potential to be integrated into standard of care to improve clinical outcomes in PCa patients.
Keywords: EED inhibitor; EZH2 signaling; chemoresistance; drug discovery; prostate cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small molecule BKM1972 inhibits human prostate cancer growth and overcomes docetaxel resistance in intraosseous models.Cancer Lett. 2019 Apr 1;446:62-72. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30660650 Free PMC article.
-
Nicardipine is a putative EED inhibitor and has high selectivity and potency against chemoresistant prostate cancer in preclinical models.Br J Cancer. 2023 Sep;129(5):884-894. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02359-y. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37474721 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb group proteins EZH2 and EED directly regulate androgen receptor in advanced prostate cancer.Int J Cancer. 2019 Jul 15;145(2):415-426. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32118. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30628724 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Modulation through the Development of EZH2-EED Interaction Inhibitors and EED Binders.J Med Chem. 2021 Aug 26;64(16):11774-11797. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00226. Epub 2021 Aug 5. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34351144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent strategies targeting Embryonic Ectoderm Development (EED) for cancer therapy: Allosteric inhibitors, PPI inhibitors, and PROTACs.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Mar 5;231:114144. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114144. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35093670 Review.
Cited by
-
Minor intron splicing is critical for survival of lethal prostate cancer.Mol Cell. 2023 Jun 15;83(12):1983-2002.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.05.017. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37295433 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular panorama of therapy resistance in prostate cancer: a pre-clinical and bioinformatics analysis for clinical translation.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Mar;43(1):229-260. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10168-9. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 38374496 Review.
-
Measurement of Bone Metastatic Tumor Growth by a Tibial Tumorigenesis Assay.Bio Protoc. 2021 Nov 20;11(22):e4231. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4231. eCollection 2021 Nov 20. Bio Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34909452 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting potential of the protein lysine and arginine methyltransferases to reverse cancer chemoresistance.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Dec 5;11:1455415. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1455415. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39703687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic and Cellular Reprogramming of Doxorubicin-Resistant MCF-7 Cells Treated with Curcumin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 14;25(24):13416. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413416. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR, Horti J, Pluzanska A, Chi KN. et al. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1502–12. - PubMed
-
- Quinn DI, Sandler HM, Horvath LG, Goldkorn A, Eastham JA. The evolution of chemotherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer. Annals of oncology: official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology. 2017;28:2658–69. - PubMed
-
- Galletti G, Leach BI, Lam L, Tagawa ST. Mechanisms of resistance to systemic therapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;57:16–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

