Serotonin/HTR1E signaling blocks chronic stress-promoted progression of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 34093864
- PMCID: PMC8171092
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.58956
Serotonin/HTR1E signaling blocks chronic stress-promoted progression of ovarian cancer
Abstract
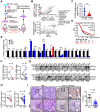
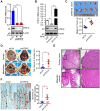
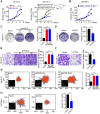
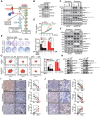
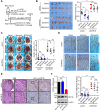
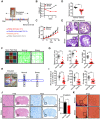
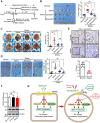
Rationale: Psychological stress has been linked to cancer development and resistance to therapy by many epidemiological and clinical studies. Stress-induced immunosuppressive microenvironment by stress hormones, in particular glucocorticoids, has been extensively studied. However, the impacts of other stress-related neurotransmitters, such as serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), on cancer development just start to be revealed. Here, we aimed to identify novel neurotransmitters involved in stress-induced growth and dissemination of ovarian cancer (OC) and reveal the major underlying signaling pathway and the therapeutic significance. Methods: Through a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screen in the murine orthotopic model of ovarian carcinoma (OC), we identified candidate genes regulating the peritoneal dissemination of OC. Among them, we picked out HTR1E, one member of 5-HT receptor family specifically expressed in the ovary and endometrium in addition to brain. The correlation of HTR1E expression with OC progression was analyzed in OC patient specimen by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), western blot, and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Gain-of-function and loss-of-function analyses were performed to explore the functions of 5-HT/HTR1E signaling in OC growth and dissemination in vitro and in vivo. In addition, we investigated the therapeutic values of HTR1E specific agonist and small molecular inhibitors against HTR1E downstream factor SRC in a stressed murine OC xenograft model. Results: In OC patients, the HTR1E expression is dramatically decreased in peritoneal disseminated OC cells, which correlates with poor clinical outcome. Silence of HTR1E in OC cells greatly promotes cell proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) by the activation of SRC-mediated downstream signaling pathways. Furthermore, chronic stress results in significantly decreased serotonin in the ovary and the enhanced OC growth and peritoneal dissemination in mice, which can be strongly inhibited by specific HTR1E agonist or the SRC inhibitor. Conclusions: We discovered the essential role of serotonin/HTR1E signaling in preventing the chronic psychological stress-promoted progression of OC, suggesting the potential therapeutic value of the HTR1E specific agonist and the SRC inhibitor for OC patients who are suffering from psychological stress.
Keywords: HTR1E; SRC; chronic stress; ovarian cancer; serotonin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Leptin as a Therapeutic Strategy against Ovarian Cancer Peritoneal Metastasis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(8):1093-1101. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666161221114454. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28002999
-
Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 and 5-HT7 receptor preferentially expressed in triple-negative breast cancer promote cancer progression through autocrine serotonin signaling.Mol Cancer. 2016 Nov 21;15(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0559-6. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27871326 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-based genome-wide screening for metastasis ability identifies FCGR1A regulating the metastatic process of ovarian cancer by targeting LSP1.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 15;150(6):306. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05837-9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38879666 Free PMC article.
-
The discovery, structure, and function of 5-HTR1E serotonin receptor.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 18;21(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01195-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37723479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin Pathway in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 28;22(3):1268. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031268. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33525332 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of serotonin-5-HTR1E signaling pathways and its role in cell survival.FASEB J. 2023 May;37(5):e22925. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300128R. FASEB J. 2023. PMID: 37078547 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the unexpected agonism of tetracyclic antidepressants at serotonin receptors 5-HT1eR and 5-HT1FR.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 19;10(16):eadk4855. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk4855. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38630816 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer and neurotransmitter receptors.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Jul 5;138(13):1540-1558. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003656. Epub 2025 May 30. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 40456676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of serotonin-5-HTR1E signaling pathways and its role in cell survival.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 27:rs.3.rs-2518076. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2518076/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: FASEB J. 2023 May;37(5):e22925. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300128R. PMID: 36789437 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Neurotransmitters: promising immune modulators in the tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 May 5;14:1118637. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1118637. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37215113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2019. 69. - PubMed
-
- Reiche EM, Nunes SO, Morimoto HK. Stress, depression, the immune system, and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:617–25. - PubMed
-
- Guereschi MG, Araujo LP, Maricato JT, Takenaka MC, Nascimento VM, Vivanco BC. et al. Beta2-adrenergic receptor signaling in CD4+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells enhances their suppressive function in a PKA-dependent manner. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43:1001–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

