Capture and displacement-based release of the bicarbonate anion by calix[4]pyrroles with small rigid straps
- PMID: 34094182
- PMCID: PMC8163245
- DOI: 10.1039/d0sc03445b
Capture and displacement-based release of the bicarbonate anion by calix[4]pyrroles with small rigid straps
Abstract
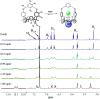
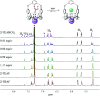
Two-phenoxy walled calix[4]pyrroles 1 and 2 strapped with small rigid linkers containing pyridine and benzene, respectively, have been synthesized. 1H NMR spectroscopic analyses carried out in CDCl3 revealed that both of receptors 1 and 2 recognize only F- and HCO3 - among various test anions with high preference for HCO3 - (as the tetraethylammonium, TEA+ salt) relative to F- (as the TBA+ salt). The bound HCO3 - anion was completely released out of the receptors upon the addition of F- (as the tetrabutylammonium, TBA+ salt) as a result of significantly enhanced affinities and selectivities of the receptors for F- once converted to the TEAHCO3 complexes. Consequently, relatively stable TEAF complexes of receptors 1 and 2 were formed via anion metathesis occurring within the receptor cavities. By contrast, the direct addition of TEAF to receptors 1 and 2 produces different complexation products initially, although eventually the same TEAF complexes are produced as via sequential TEAHCO3 and TBAF addition. These findings are rationalized in terms of the formation of different ion pair complexes involving interactions both inside and outside of the core receptor framework.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures






References
-
- Sessler J. L., Gale P. A. and Cho W.-S., Anion Receptor Chemistry, ed. J. F. Stoddart, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2006
- Bianchi A., Bowman-James K. and García-España E., Supramolecular Chemistry of Anions, Wiley-VCH, New York, 1997
- Anion Coordination Chemistry, ed. K. Bowman-James, A. Bianchi and E. García-España, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011
-
- Beer P. D. Gale P. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001;40:486–516. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010202)40:3<486::AID-ANIE486>3.0.CO;2-P. - DOI - PubMed
- Martínez-Máñez R. Sancenán F. Chem. Rev. 2003;103:4419–4476. doi: 10.1021/cr010421e. - DOI - PubMed
- Gale P. A. Busschaert N. Haynes C. J. E. Karagiannidis L. E. Kirby I. L. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014;43:205–241. doi: 10.1039/C3CS60316D. - DOI - PubMed
- Wenzel M. Hiscock J. R. Gale P. A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012;41:480–520. doi: 10.1039/C1CS15257B. - DOI - PubMed
- Gale P. A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010;39:3746–3771. doi: 10.1039/C001871F. - DOI - PubMed
- Caltagirone C. Gale P. A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009;38:520–563. doi: 10.1039/B806422A. - DOI - PubMed
- Gale P. A. Caltagirone G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015;44:4212–4227. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00179F. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kang S. O. Begum R. A. Bowman-James K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2006;45:7882–7894. doi: 10.1002/anie.200602006. - DOI - PubMed
- Kang S. O. Llinares J. M. Day V. W. Bowman-James K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010;39:3980–4003. doi: 10.1039/C0CS00083C. - DOI - PubMed
- Oh J. H. Kim J. H. Kim D. S. Han H. J. Lynch V. M. Sessler J. L. Kim S. K. Org. Lett. 2019;21:4336–4339. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01515. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Y. Cann M. J. Litvin T. N. Iourgenko V. Sinclair M. L. Levin L. R. Buck J. Science. 2000;289:625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5479.625. - DOI - PubMed
- Krieg B. J. Taghavi S. M. Amidon G. L. Amidon G. E. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014;103:3473–3490. doi: 10.1002/jps.24108. - DOI - PubMed
- Vaughan-Jones R. D. Spitzer K. W. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002;80:579–596. doi: 10.1139/o02-157. - DOI - PubMed
- Roos A. Boron W. F. Physiol. Rev. 1981;61:296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. - DOI - PubMed
- Zippin J. H. Levin L. R. Buck J. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;12:366–370. doi: 10.1016/S1043-2760(01)00454-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

