Towards efficient discovery of green synthetic pathways with Monte Carlo tree search and reinforcement learning
- PMID: 34094345
- PMCID: PMC8162445
- DOI: 10.1039/d0sc04184j
Towards efficient discovery of green synthetic pathways with Monte Carlo tree search and reinforcement learning
Abstract
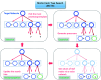
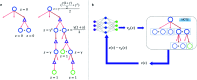
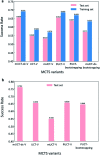
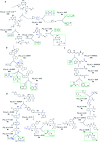
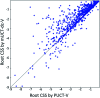
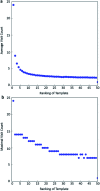
Computer aided synthesis planning of synthetic pathways with green process conditions has become of increasing importance in organic chemistry, but the large search space inherent in synthesis planning and the difficulty in predicting reaction conditions make it a significant challenge. We introduce a new Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) variant that promotes balance between exploration and exploitation across the synthesis space. Together with a value network trained from reinforcement learning and a solvent-prediction neural network, our algorithm is comparable to the best MCTS variant (PUCT, similar to Google's Alpha Go) in finding valid synthesis pathways within a fixed searching time, and superior in identifying shorter routes with greener solvents under the same search conditions. In addition, with the same root compound visit count, our algorithm outperforms the PUCT MCTS by 16% in terms of determining successful routes. Overall the success rate is improved by 19.7% compared to the upper confidence bound applied to trees (UCT) MCTS method. Moreover, we improve 71.4% of the routes proposed by the PUCT MCTS variant in pathway length and choices of green solvents. The approach generally enables including Green Chemistry considerations in computer aided synthesis planning with potential applications in process development for fine chemicals or pharmaceuticals.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A self-learning Monte Carlo tree search algorithm for robot path planning.Front Neurorobot. 2023 Jul 6;17:1039644. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2023.1039644. eCollection 2023. Front Neurorobot. 2023. PMID: 37483541 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient retrosynthetic planning with MCTS exploration enhanced A* search.Commun Chem. 2024 Mar 7;7(1):52. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01133-2. Commun Chem. 2024. PMID: 38454002 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Drug Design Using Transformer-Based Machine Translation and Reinforcement Learning of an Adaptive Monte Carlo Tree Search.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 27;17(2):161. doi: 10.3390/ph17020161. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399376 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging green synthetic routes for thiazole and its derivatives: Current perspectives.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2024 Feb;357(2):e2300420. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202300420. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2024. PMID: 38013395 Review.
-
How Can Deep Eutectic Systems Promote Greener Processes in Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery?Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;17(2):221. doi: 10.3390/ph17020221. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399436 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retrosynthetic planning with experience-guided Monte Carlo tree search.Commun Chem. 2023 Jun 10;6(1):120. doi: 10.1038/s42004-023-00911-8. Commun Chem. 2023. PMID: 37301940 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Monte Carlo Tree Search for Retrosynthesis.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jul 14;65(13):6537-6546. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00417. Epub 2025 Jun 13. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 40512567 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive chemistry: machine learning for reaction deployment, reaction development, and reaction discovery.Chem Sci. 2022 Nov 28;14(2):226-244. doi: 10.1039/d2sc05089g. eCollection 2023 Jan 4. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 36743887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Learning in continuous action space for developing high dimensional potential energy models.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 18;13(1):368. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27849-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35042872 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Methods and Models for Retro-Biosynthesis: A Scoping Review.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Aug 16;13(8):2276-2294. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00091. Epub 2024 Jul 24. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 39047143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Segler M. H. S. Preuss M. Waller M. P. Nature. 2018;555:604–610. - PubMed
-
- Baylon J. L. Cilfone N. A. Gulcher J. R. Chittenden T. W. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019;59:673–688. - PubMed
-
- Cook A. Johnson A. P. Law J. Mirzazadeh M. Ravitz O. Simon A. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012;2:79–107.
-
- Szymkuć S. Gajewska E. P. Klucznik T. Molga K. Dittwald P. Startek M. Bajczyk M. Grzybowski B. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016;55:5904–5937. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

