The renal patient seen by non-renal physicians: the kidney embedded in the 'milieu intérieur'
- PMID: 34094517
- PMCID: PMC8173597
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa234
The renal patient seen by non-renal physicians: the kidney embedded in the 'milieu intérieur'
Abstract
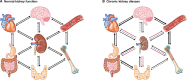
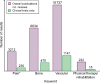
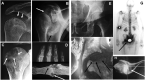
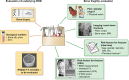
Chronic kidney disease is defined as a decrease in renal function or evidence of kidney injury for >3 months. This represents an oversimplification that may confuse physicians. Thus kidney function is equated to glomerular filtration rate, which represents one of multiple kidney functions. Some potentially more important renal functions are lost earlier, such as the production for the anti-ageing factor Klotho. Overall, these changes modify the emergent properties of the body, altering the relationships between different organs and systems, in a manner that is difficult to predict the response to interventions based on normal physiology concepts, as there is a novel steady state of interorgan relations. In this regard we now discuss the impact of CKD on heart failure; osteomuscular and joint pain and bone fragility and fractures; and osteosarcopaenia as seen by a cardiologist, a rheumatologist and a geriatrician.
Keywords: bone fragility; chronic kidney disease; emergence; fracture; heart failure; network disease; osteosarcopaenia.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The risk of new fragility fractures in patients with chronic kidney disease and hip fracture-a population-based cohort study in the UK.Osteoporos Int. 2020 Aug;31(8):1487-1497. doi: 10.1007/s00198-020-05351-x. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Osteoporos Int. 2020. PMID: 32266436 Free PMC article.
-
The role of klotho in chronic kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Oct 22;19(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-1094-z. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30348110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of kidney protective factors by inflammation: role of transcription factors and epigenetic mechanisms.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):F1329-F1340. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00487.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27760772 Review.
-
Plasma s-Klotho is related to kidney function and predicts adverse renal outcomes in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease.J Investig Med. 2018 Mar;66(3):669-675. doi: 10.1136/jim-2017-000560. Epub 2017 Oct 23. J Investig Med. 2018. PMID: 29061648
-
[Electrolyte and acid-base balance disorders in advanced chronic kidney disease].Nefrologia. 2008;28 Suppl 3:87-93. Nefrologia. 2008. PMID: 19018744 Spanish.
References
-
- National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 2002; 39(2 Suppl 1): S1–S266 - PubMed
-
- Vanholder R, Massy Z, Argiles A. et al. Chronic kidney disease as cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005; 20: 1048–1056 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

