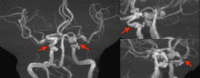
Dual aortic aneurysms with coronary artery and multiple cerebrovascular stenoses
- PMID: 34094555
- PMCID: PMC8163995
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.4087
Dual aortic aneurysms with coronary artery and multiple cerebrovascular stenoses
Abstract
Total debranching thoracic endovascular aortic repair is useful for avoiding neurological complications in cases where cardiopulmonary bypass is difficult and for devising an intraoperative cervical branch reconstruction method.
Keywords: abdominal aortic aneurysm; cardiopulmonary bypass; thoracic aortic aneurysm.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors certify that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of custom Dacron branch grafts for "hybrid" aortic debranching during endovascular repair of thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008 Jul;136(1):21-8, 28.e1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.02.051. Epub 2008 May 7. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008. PMID: 18603048
-
Follow-up results of aortic arch cervical debranching performed with the help of a temporary crossover external carotid artery bypass for cerebral protection followed by endovascular thoracic aortic aneurysm repair.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2020 May 1;30(5):724-731. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivaa004. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32073125
-
Midterm Outcomes of Endovascular Repair of Aortic Arch Aneurysms with the Gore Thoracic Branch Endoprosthesis.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2022 Dec;64(6):639-645. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2022.08.003. Epub 2022 Aug 13. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 35970335 Clinical Trial.
-
Combined abdominal aortic aneurysm repair and coronary artery bypass: presentation of 13 cases and review of the literature.Ann Vasc Surg. 2006 Jan;20(1):23-9. doi: 10.1007/s10016-005-9324-9. Ann Vasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 16378145 Review.
-
Complications of endovascular aneurysm repair of the thoracic and abdominal aorta: evaluation and management.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2018 Apr;8(Suppl 1):S138-S156. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2017.09.17. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2018. PMID: 29850426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Type A Acute Aortic Dissection Presenting With Arch and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms.Cureus. 2023 Sep 4;15(9):e44629. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44629. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37799248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castelli P, Caronn R, Piffaretti G, et al. Endovascular repair for concomitant multilevel aortic disease. Eur J Card Thorac Surg. 2005;28:478‐482. - PubMed
-
- Moon MR, Mitchell RS, Dake MD, Zarins CK, Fann JI, Miller DC. Simultaneous abdominal aortic replacement and thoracic stent graft placement for multilevel aortic disease. J Vasc Surg. 1997;25:332‐340. - PubMed
-
- Lucas LA, Rodriguez‐Lopez JA, Olsen DM, Diethrich EB. Endovascular repair in the thoracic and abdominal aorta: no increased risk of spinal cord ischemia when both territories are treated. J Endovas Ther. 2009;16:189‐196. - PubMed
-
- Kato M, Kagaya H, Kubo Y, Banno H, Ohkubo N. Real chimney technique for total debranching of supra‐aortic trunk. J Vasc Surg. 2015;61:542‐545. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

