Tolvaptan Response in a Hyponatremic Newborn with Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone
- PMID: 34094612
- PMCID: PMC8137302
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9920817
Tolvaptan Response in a Hyponatremic Newborn with Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone
Abstract
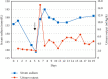
The use of tolvaptan to treat both euvolemic and hypervolemic hyponatremia has rapidly increased in recent years. However, data on its effects on children, especially newborns and infants, are limited. Here, we present a newborn who developed syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone following an intracranial hematoma drainage operation who was unresponsive to conventional treatments. The infant was successfully treated with tolvaptan, a competitive inhibitor of the vasopressin V2 receptor.
Copyright © 2021 Cengiz Zeybek et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources