Deficiency of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Exacerbates Brain Damage and Cognitive Deficit in A Mouse Model of Vascular Dementia
- PMID: 34094639
- PMCID: PMC8139201
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2020.0523
Deficiency of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Exacerbates Brain Damage and Cognitive Deficit in A Mouse Model of Vascular Dementia
Abstract
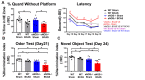
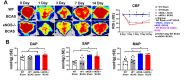
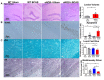
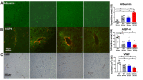
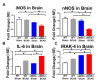
Vascular Dementia (VaD) accounts for nearly 20% of all cases of dementia. eNOS plays an important role in neurovascular remodeling, anti-inflammation, and cognitive functional recovery after stroke. In this study, we investigated whether eNOS regulates brain damage, cognitive function in mouse model of bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS) induced VaD. Late-adult (6-8 months) C57BL/6J and eNOS knockout (eNOS-/-) mice were subjected to BCAS (n=12/group) or sham group (n=8/group). BCAS was performed by applying microcoils to both common carotid arteries. Cerebral blood flow (CBF) and blood pressure were measured. A battery of cognitive functional tests was performed, and mice were sacrificed 30 days after BCAS. Compared to corresponding sham mice, BCAS in wild-type (WT) and eNOS-/- mice significantly: 1) induces short term, long term memory loss, spatial learning and memory deficits; 2) decreases CBF, increases ischemic cell damage, including apoptosis, white matter (WM) and axonal damage; 3) increases blood brain barrier (BBB) leakage, decreases aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression and vessel density; 4) increases microglial, astrocyte activation and oxidative stress in the brain; 5) increases inflammatory factor interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1(IRAK-1) and amyloid beta (Aβ) expression in brain; 6) increases IL-6 and IRAK4 expression in brain. eNOS-/-sham mice exhibit increased blood pressure, decreased iNOS and nNOS in brain compared to WT-sham mice. Compared to WT-BCAS mice, eNOS-/-BCAS mice exhibit worse vascular and WM/axonal damage, increased BBB leakage and inflammatory response, increased cognitive deficit, decreased iNOS, nNOS in brain. eNOS deficit exacerbates BCAS induced brain damage and cognitive deficit.
Keywords: Vascular dementia; bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS); endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS); white matter injury.
copyright: © 2021 An et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cardiac Dysfunction in a Mouse Vascular Dementia Model of Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Stenosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 11;8:681572. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.681572. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34179145 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 is a novel target molecule for cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Mar;34(3):616-25. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302440. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24371084
-
Chronic Remote Ischemic Conditioning Is Cerebroprotective and Induces Vascular Remodeling in a VCID Model.Transl Stroke Res. 2018 Feb;9(1):51-63. doi: 10.1007/s12975-017-0555-1. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Transl Stroke Res. 2018. PMID: 28755277 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunction of Cerebrovascular Endothelial Cells: Prelude to Vascular Dementia.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Nov 16;10:376. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00376. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30505270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene knockout mice.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999 Nov;32(11):1353-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1999001100005. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999. PMID: 10559836 Review.
Cited by
-
Anxiolytic-like Activity, Antioxidant Properties, and Facilitatory Effects on the Short-Term Memory Retention of Molsidomine in Rats.Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;14(3):306. doi: 10.3390/life14030306. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541632 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Alleviates Demyelination Through Regulating Microglial Phenotype Transformation to Mitigate Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Mice with Vascular Dementia.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 May;59(5):3140-3158. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02712-3. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35267135
-
Magnesium and the Brain: A Focus on Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 23;24(1):223. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010223. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Betaine protects cerebral microvascular endothelium and ameliorates hypertension-induced cognitive dysfunction via upregulation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase/nitric monoxide signaling pathway.J Hypertens. 2025 Sep 1;43(9):1529-1538. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000004085. Epub 2025 Jun 16. J Hypertens. 2025. PMID: 40530574 Free PMC article.
-
The Unexpected Role of the Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase at the Neurovascular Unit: Beyond the Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9071. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169071. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi BR, Kim DH, Back DB, Kang CH, Moon WJ, Han JS, et al.. (2016). Characterization of White Matter Injury in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Stroke, 47:542-547. - PubMed
-
- Miki K, Ishibashi S, Sun L, Xu H, Ohashi W, Kuroiwa T, et al.. (2009). Intensity of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion determines white/gray matter injury and cognitive/motor dysfunction in mice. J Neurosci Res, 87:1270-1281. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
