Isolated Unilateral Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy Caused by Internal Carotid Artery Loop
- PMID: 34094773
- PMCID: PMC8171351
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14819
Isolated Unilateral Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy Caused by Internal Carotid Artery Loop
Abstract
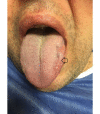
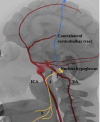
Isolated unilateral hypoglossal nerve (HN) palsy caused by vascular compression is a rare condition. We report a case of a 42-year-old male, presenting with tongue paresis and unilateral atrophy of the tongue due to an internal carotid artery (ICA) loop. The compression of HN by ICA loop and concomitant wall irregularities of the loop segment were observed in magnetic resonance imaging and digital subtraction angiography (DSA). The patient was managed with antithrombotic without the need of any further intervention. To our best knowledge, this is the first reported case of isolated compressive neuropathy of the HN caused by loop of the ICA. Here, the clinical presentation, etiology, and management of isolated HN palsy caused by vascular lesions are discussed along with the relevant literature.
Keywords: carotid artery dissection; cerebral angiography; internal carotid artery loop; isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy; vascular compression.
Copyright © 2021, Dokdok et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hypoglossal nerve palsy due to internal carotid artery dissection with pseudoaneurysm formation: An unusual presentation.Acta Radiol Open. 2022 Jun 24;11(6):20584601221111701. doi: 10.1177/20584601221111701. eCollection 2022 Jun. Acta Radiol Open. 2022. PMID: 35782990 Free PMC article.
-
Carotid artery stenting for spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection presenting with hypoglossal nerve palsy: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2022 May 27;13:225. doi: 10.25259/SNI_184_2022. eCollection 2022. Surg Neurol Int. 2022. PMID: 35673643 Free PMC article.
-
Unilateral spontaneous dissection of the internal carotid artery presenting as hypoglossal nerve palsy.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2004 Aug;261(7):405-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-003-0696-6. Epub 2003 Oct 24. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2004. PMID: 14576950
-
Hypoglossal nerve palsy as an isolated syndrome of internal carotid artery dissection: A review of the literature and a case report.Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2018 Nov-Dec;52(6):731-735. doi: 10.1016/j.pjnns.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2018. PMID: 30082078 Review.
-
Surgical Treatment of Spontaneous Internal Carotid Artery Dissection with Abducent Nerve Palsy: Case Report and Review of Literature.World Neurosurg. 2019 May;125:10-14. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.096. Epub 2019 Jan 31. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30711658 Review.
Cited by
-
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia and hypoglossal nerve palsy: A singular clinical case of two rare concomitant neurovascular conflicts.Surg Neurol Int. 2025 Apr 25;16:153. doi: 10.25259/SNI_55_2025. eCollection 2025. Surg Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40353176 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglossal Nerve Neuropathies-Analysis of Causes and Anatomical Background.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 14;12(4):864. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040864. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hypoglossal nerve palsy as an isolated syndrome of internal carotid artery dissection: a review of the literature and a case report. Mes M, Palczewski P, Szczudlik P, Łusakowska A, Maj E, Gawel M. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2018;52:731–735. - PubMed
-
- Imaging features of isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy. Guarnizo A, Glikstein R, Torres C. J Neuroradiol. 2020;47:136–150. - PubMed
-
- Hypoglossal nerve palsy: 245 cases. Stino AM, Smith BE, Temkit M, Reddy SN. Muscle Nerve. 2016;54:1050–1054. - PubMed
-
- Kim SY, Naqvi IA. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Neuroanatomy, Cranial Nerve 12 (Hypoglossal) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
