Spontaneous Rupture of Empyema Necessitans in the Emergency Department
- PMID: 34094776
- PMCID: PMC8172015
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14822
Spontaneous Rupture of Empyema Necessitans in the Emergency Department
Abstract
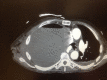
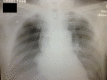
An empyema necessitans is a rare complication of a collection of purulent material in the pleural space that spreads outside of the pleural cavity and involves the soft tissues of the chest wall. Due to compression forces created by the size of the collection of empyema in the chest cavity, patients are usually symptomatic and present with severe dyspnea. Chest X-ray or ultrasound of the chest cavity are the ideal screening tools to visualize the empyema and followed by computerized tomography scan of the chest to confirm the presence and extent of the pathology. In rare occasions, the empyema can rupture spontaneously, which may lead to critical situation requiring emergent intervention. We report the case of a 72-year-old male who presented to the emergency department with severe dyspnea and was diagnosed with empyema necesitans. During the initial management of the case, the empyema necessitans ruptured spontaneously and required emergent interventions to stabilize the patient.
Keywords: computerized tomography; empyema; empyema necessitans; rupture of empyema; thoracostomy tube.
Copyright © 2021, Crouch et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Necrotizing fasciitis of the chest wall caused by empyema necessitans following tuberculosis: Case report and literature review.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 May;106:108300. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108300. Epub 2023 May 4. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37150161 Free PMC article.
-
Empyema Necessitans Diagnosed by Point-of-Care Ultrasound.J Emerg Med. 2020 Dec;59(6):e221-e223. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2020.09.020. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 33059991
-
Empyema Necessitans: A Rare Complication of Chest Drains.Cureus. 2024 Sep 22;16(9):e69931. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69931. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39439608 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual presentation of empyema necessitans: case report and review of the literature.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021 Jun;69(6):1026-1030. doi: 10.1007/s11748-021-01601-9. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33559044 Review.
-
Silicone thorax: a complication of tube thoracostomy in the presence of mammary implants.Ann Thorac Surg. 1995 Nov;60(5):1417-9. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(95)00499-B. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995. PMID: 8526644 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare Escherichia coli Empyema Necessitating to Pelvic Retroperitoneum With Extension to the Groin.Cureus. 2023 Oct 22;15(10):e47467. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47467. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021685 Free PMC article.
-
Unilateral Unusual Post-traumatic Breast Pain and Swelling in a Young Adult: A Case of Tuberculous Empyema Necessitans.Cureus. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):e66914. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66914. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39280503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A new classification of parapneumonic effusions and empyema. Light RW. Chest. 1995;108:299–301. - PubMed
-
- Risk factors for complicated parapneumonic effusion and empyema on presentation to hospital with community-acquired pneumonia. Chalmers JD, Singanayagam A, Murray MP, Scally C, Fawzi A, Hill AT. Thorax. 2009;64:592–597. - PubMed
-
- Predictive factors, microbiology and outcome of patients with parapneumonic effusion. Falguera M, Carratalà J, Bielsa S, et al. Eur Respir J. 2011;38:1173–1179. - PubMed
-
- Diagnostic utility and clinical application of imaging for pleural space infections. Heffner JE, Klein JS, Hampson C. Chest. 2010;137:467–479. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources