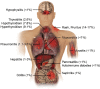
Organ-Specific Immune-Related Adverse Events for PD-1 Antibodies in Lung Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 34094910
- PMCID: PMC8175899
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.628243
Organ-Specific Immune-Related Adverse Events for PD-1 Antibodies in Lung Cancer Treatment
Abstract
Anti-PD-1 therapy has revolutionized the clinical treatment of lung cancer. With the increasing number of lung cancer patients being treated, there is also an increase in the number of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) being reported. These irAEs involve multiple organs and systems, mainly manifest as inflammatory side effects, and are different from the adverse events observed with traditional lung cancer treatment. These effects are often mild and treatable and reversible; however, in a few cases the side effects can be severe and lead to termination of immunotherapy. Management involves glucocorticoid-based related immunomodulators, which should be carefully prescribed to balance the efficacy and side effects of the PD-1 antibody treatment. This review will describe the characteristics and mechanisms of irAEs in specific organs, and will serve as a guide to help optimize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: PD-1 antibody therapy; immune-related adverse events (irAE); inflammatory; lung cancer; side effect.
Copyright © 2021 Zheng and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune-related adverse events associated with programmed cell death protein-1 and programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer: a PRISMA systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jun 10;19(1):558. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5701-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31182061 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Immune-Related Adverse Events with Clinical Benefit in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Nivolumab.Oncologist. 2018 Nov;23(11):1358-1365. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0384. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Oncologist. 2018. PMID: 29934411 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-related adverse events predict the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibodies in cancer patients.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Mar;109:21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.10.014. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30682533
-
New insight in endocrine-related adverse events associated to immune checkpoint blockade.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jan;34(1):101370. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2019.101370. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31983543 Review.
-
Management of Adverse Events Following Treatment With Anti-Programmed Death-1 Agents.Oncologist. 2016 Oct;21(10):1230-1240. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0055. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27401894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive Biomarkers of Severe Immune-Related Adverse Events With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Prevention, Underlying Causes, Intensity, and Consequences.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 14;9:908752. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.908752. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35774996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing cancer care with improved checkpoint inhibitors: a focus on PD-1/PD-L1.EXCLI J. 2024 Oct 29;23:1303-1326. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7783. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 39624113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources