Variation of Long Non-Coding RNA And mRNA Profiles in Breast Cancer Cells With Influences of Adipocytes
- PMID: 34094912
- PMCID: PMC8176020
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.631551
Variation of Long Non-Coding RNA And mRNA Profiles in Breast Cancer Cells With Influences of Adipocytes
Abstract
Background: It is well known that obesity is one of the risks for incurrence and development in breast cancer patients. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are reported to participate in the composition of tumor microenvironment and to regulate breast cancer cell metabolic activities. However, there was rare study focused on the lncRNAs in breast cancer with the influences of adipocytes. The study aimed to investigate lncRNAs expression profiles and discover potential biomarkers to predict the incidence and progression of adipocyte-associated-breast cancer.
Methods: We co-cultured adipocytes with breast cancer cells and profiled the expression of lncRNAs as well as mRNAs by using the RNA-sequencing method. Wound Healing, Migration assays and Invasion assays were applied to verify the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells.
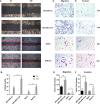
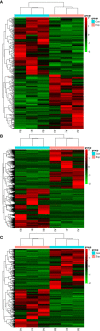
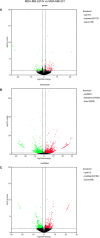
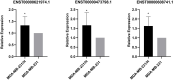
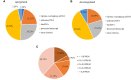
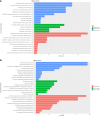
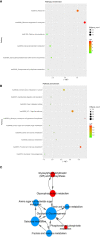
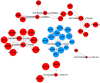
Results: MDA-MB-231/Hpa-V and SK-BR-3/Hpa-V cells showed elevated migration and invasiveness compared to the control group. A sum of 371 mRNAs (181 upregulated and 190 downregulated) and 850 lncRNAs(414 upregulated and 436 downregulated) were differentially expressed in MDA-MB-231/Hpa-V comparing to MDA-MB-231(P < 0.05; |log2 (fold change)|>1.2). GO enrichment, KEGG pathway and interaction networks demonstrated that differentially expressed lncRNAs were involved in functional categories, such as material metabolism, which might lead to the progression of breast cancer.
Conclusion: Our study detected a lncRNA profile in breast cancer cells affecting by adipocytes and provided a better understanding of the tumor microenvironment. LncRNAs may be helpful to predict the therapeutic responses and prognosis of obese breast cancer patients.
Keywords: adipocytes; breast cancer; long-non-coding RNA; mRNA; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Cao, Yang, Liang, Ma, Xu, Fei, Zhang, Chen and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct long non-coding RNA and mRNA expression profiles in the hippocampus of an attention deficit hyperactivity disorder model in spontaneously hypertensive rats and control wistar Kyoto rats.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Aug;161:177-196. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.03.015. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32344128
-
Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs in breast cancer brain metastasis.Epigenomics. 2021 Jul;13(14):1113-1128. doi: 10.2217/epi-2021-0152. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Epigenomics. 2021. PMID: 34148372
-
Integrated Transcriptome Analysis of Human Visceral Adipocytes Unravels Dysregulated microRNA-Long Non-coding RNA-mRNA Networks in Obesity and Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 2;10:1089. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01089. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32714872 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs: implications in targeted diagnoses, prognosis, and improved therapeutic strategies in human non- and triple-negative breast cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Jun 27;10:88. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0514-z. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29983835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer metastasis.Noncoding RNA Res. 2020 Nov 16;5(4):208-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2020.11.004. eCollection 2020 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020. PMID: 33294746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of a prognostic score model for breast cancer based on multi-omics analysis of study on bone metastasis.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 May 31;13(5):2419-2436. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1881. Epub 2024 May 20. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38881940 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocytes promote metastasis of breast cancer by attenuating the FOXO1 effects and regulating copper homeostasis.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Aug 12;24(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03433-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39135158 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications in obesity-associated diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Feb 24;5(2):e496. doi: 10.1002/mco2.496. eCollection 2024 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38405061 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

