XGBoost Classifier Based on Computed Tomography Radiomics for Prediction of Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T-Cells in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34094971
- PMCID: PMC8170309
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.671333
XGBoost Classifier Based on Computed Tomography Radiomics for Prediction of Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T-Cells in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: This study constructed and validated a machine learning model to predict CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte expression levels in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) using computed tomography (CT) radiomic features.
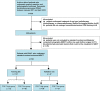
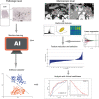
Materials and methods: In this retrospective study, 184 PDAC patients were randomly assigned to a training dataset (n =137) and validation dataset (n =47). All patients were divided into CD8+ T-high and -low groups using X-tile plots. A total of 1409 radiomics features were extracted from the segmentation of regions of interest, based on preoperative CT images of each patient. The LASSO algorithm was applied to reduce the dimensionality of the data and select features. The extreme gradient boosting classifier (XGBoost) was developed using a training set consisting of 137 consecutive patients admitted between January 2017 and December 2017. The model was validated in 47 consecutive patients admitted between January 2018 and April 2018. The performance of the XGBoost classifier was determined by its discriminative ability, calibration, and clinical usefulness.
Results: The cut-off value of the CD8+ T-cell level was 18.69%, as determined by the X-tile program. A Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated a correlation between higher CD8+ T-cell levels and better overall survival (p = 0.001). The XGBoost classifier showed good discrimination in the training set (area under curve [AUC], 0.75; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.67-0.83) and validation set (AUC, 0.67; 95% CI: 0.51-0.83). Moreover, it showed a good calibration. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values were 80.65%, 60.00%, 0.69, 0.63, and 0.79, respectively, for the training set, and 80.95%, 57.69%, 0.68, 0.61, and 0.79, respectively, for the validation set.
Conclusions: We developed a CT-based XGBoost classifier to extrapolate the infiltration levels of CD8+ T-cells in patients with PDAC. This method could be useful in identifying potential patients who can benefit from immunotherapies.
Keywords: CD8 positive T lymphocytes; contrast-enhanced computed tomography images; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; prognosis; radiomics.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Shi, Liu, Fang, Cao, Meng, Zhang, Yu, Feng, Li, Liu, Wang, Jiang, Lu, Shao and Bian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Machine Learning for Computed Tomography Radiomics: Prediction of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Pancreas. 2022 May 1;51(5):549-558. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000002069. Epub 2022 Jul 24. Pancreas. 2022. PMID: 35877153
-
CT Radiomics and Machine-Learning Models for Predicting Tumor-Stroma Ratio in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 8;11:707288. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.707288. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34820324 Free PMC article.
-
CT radiomics signature: a potential biomarker for fibroblast activation protein expression in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022 Aug;47(8):2822-2834. doi: 10.1007/s00261-022-03512-6. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35451626
-
Preoperative Radiomics Approach to Evaluating Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Mar;55(3):803-814. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27871. Epub 2021 Aug 6. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34355834
-
Machine learning for MRI radiomics: a study predicting tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Oct;46(10):4800-4816. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03159-9. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 34189612
Cited by
-
Radiomics features for assessing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes correlate with molecular traits of triple-negative breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2022 Oct 15;20(1):471. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03688-x. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36243806 Free PMC article.
-
MORE: a multi-omics data-driven hypergraph integration network for biomedical data classification and biomarker identification.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Nov 22;26(1):bbae658. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae658. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39692449 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning: A non-invasive prediction method for gastric cancer based on a survey of lifestyle behaviors.Front Artif Intell. 2022 Aug 16;5:956385. doi: 10.3389/frai.2022.956385. eCollection 2022. Front Artif Intell. 2022. PMID: 36052291 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging-Based Biomarkers Predict Programmed Death-Ligand 1 and Survival Outcomes in Advanced NSCLC Treated With Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab: A Multi-Institutional Study.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023 Nov 18;4(12):100602. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2023.100602. eCollection 2023 Dec. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 38124790 Free PMC article.
-
Non-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics model for the differentiation of pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 23;13:1108545. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1108545. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36756153 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

