Facile Synthesis of Pd@PtM (M = Rh, Ni, Pd, Cu) Multimetallic Nanorings as Efficient Catalysts for Ethanol Oxidation Reaction
- PMID: 34095088
- PMCID: PMC8170318
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.683450
Facile Synthesis of Pd@PtM (M = Rh, Ni, Pd, Cu) Multimetallic Nanorings as Efficient Catalysts for Ethanol Oxidation Reaction
Abstract
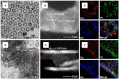
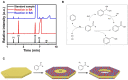
Pt-based multimetallic nanorings with a hollow structure are attractive as advanced catalysts due to their fantastic structure feature. However, the general method for the synthesis of such unique nanostructures is still lack. Here we report the synthesis of Pd@PtM (M = Rh, Ni, Pd, Cu) multimetallic nanorings by selective epitaxial growth of Pt alloyed shells on the periphery of Pd nanoplates in combination with oxidative etching of partial Pd in the interior. In situ generation of CO and benzoic acid arising from interfacial catalytic reactions between Pd nanoplates and benzaldehyde are critical to achieve high-quality Pt-based multimetallic nanorings. Specifically, the in-situ generated CO promotes the formation of Pt alloyed shells and their epitaxial growth on Pd nanoplates. In addition, the as-formed benzoic acid and residual oxygen are responsible for selective oxidative etching of partial Pd in the interior. When evaluated as electrocatalysts, the Pd@PtRh nanorings exhibit remarkably enhanced activity and stability for ethanol oxidation reaction (EOR) compared to the Pd@PtRh nanoplates and commercial Pt/C due to their hollow nanostructures.
Keywords: electrocatalysis; epitaxial growth; interfacial catalytic reactions; multimetallic nanocrystals; nanorings.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Li, Yan, Luo, Huang, Li, Yang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epitaxial Growth of Multimetallic Pd@PtM (M = Ni, Rh, Ru) Core-Shell Nanoplates Realized by in Situ-Produced CO from Interfacial Catalytic Reactions.Nano Lett. 2016 Dec 14;16(12):7999-8004. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b04524. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Nano Lett. 2016. PMID: 27960487
-
Ultrathin Two-Dimensional Pd-Based Nanorings as Catalysts for Hydrogenation with High Activity and Stability.Small. 2015 Sep;11(36):4745-52. doi: 10.1002/smll.201500769. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Small. 2015. PMID: 26150015
-
A universal synthesis of ultrathin Pd-based nanorings for efficient ethanol electrooxidation.Mater Horiz. 2023 Apr 3;10(4):1416-1424. doi: 10.1039/d2mh01363k. Mater Horiz. 2023. PMID: 36779279
-
Pt-Based Catalysts for Electrochemical Oxidation of Ethanol.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2019 Apr 4;377(3):11. doi: 10.1007/s41061-019-0236-5. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2019. PMID: 30949779 Review.
-
Design of Ultrathin Pt-Based Multimetallic Nanostructures for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis.Small. 2017 Dec;13(48). doi: 10.1002/smll.201702156. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Small. 2017. PMID: 29116672 Review.
References
-
- Brouzgou A., Podias A., Tsiakaras P. (2012). PEMFCs and AEMFCs directly fed with ethanol: a current status comparative review. J. Appl. Electrochem. 43, 119–136. 10.1007/s10800-012-0513-2 - DOI
-
- De Souza J. P. I., Queiroz S. L., Bergamaski K., Gonzalez E. R., Nart F. C. (2002). Electro-oxidation of ethanol on Pt, Rh, and PtRh electrodes. A study using DEMS and in-situ FTIR techniques. J. Phys. Chem. B 106:9825. 10.1021/jp014645c - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

