TGFβ1 in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Is Associated With Progression and Radiosensitivity in Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 34095135
- PMCID: PMC8172974
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.667645
TGFβ1 in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Is Associated With Progression and Radiosensitivity in Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Objective: Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is aggressive, with early metastasis. Cytokines secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) within various tumors influences these features, but the function in particular of TGFβ1 (transforming growth factor beta 1) is controversial and unknown in SCLC. This study explored the influence of TGFβ1 in CAFs on the development, immune microenvironment, and radiotherapy sensitivity of SCLC.
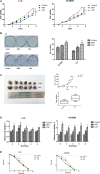
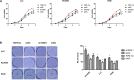
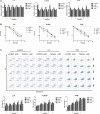
Methods: SCLC specimens were collected from 90 patients who had received no treatment before surgery. Tumor and tumor stroma were subjected to multiplex immunohistochemistry to quantitate TGFβ1 and other immune factors in CAFs. Cell proliferation and flow cytometry apoptosis assays were used to investigate associations between TGFβ1 and proliferation and radiotherapy sensitivity. The immune factors in tumors were detected by immunohistochemistry in vitro and in vivo (mice).
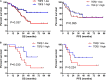
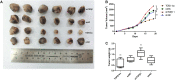
Results: TGFβ1 levels on CAFs lower or higher than the median were found, respectively, in 52.2 and 47.8% of patients; overall survival of patients with TGFβ1-high levels (53.9 mo) was significantly longer than that of the TGFβ1-low group (26.9 mo; P = 0.037). The univariate and multivariate analyses indicated that a TGFβ1-high level was an independent predictor of increased survival time. TGFβ1-high levels in CAFs were associated with inhibition of growth, proliferation, antitumor immunity, and enhanced radiotherapeutic sensitivity and tumor immunity of tumor. TGFβ1-low levels promoted tumor cell growth and radiotherapy sensitivity in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusion: High levels of TGFβ1 in CAFs were associated with longer overall survival in patients with SCLC and enhanced radiotherapy sensitivity.
Keywords: TGFβ1; cancer-associated fibroblasts; immune microenvironment; prognostic marker; radiotherapy sensitivity; small-cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Qi, Wei, Lei, Yu, Liu, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts mediated chemoresistance by a FOXO1/TGFβ1 signaling loop in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Mar;56(3):1150-1163. doi: 10.1002/mc.22581. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 27769097
-
Co-migration of colon cancer cells and CAFs induced by TGFβ₁ enhances liver metastasis.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Mar;359(3):829-39. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2075-6. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25557989
-
Podoplanin-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibit small cell lung cancer growth.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):9531-41. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3371. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25909164 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cancer-associated fibroblasts on radiosensitivity of cancer cells.Future Oncol. 2017 Jul;13(17):1537-1550. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0054. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Future Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28685611 Review.
-
Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives.Mol Cancer. 2021 Oct 11;20(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01428-1. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34635121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Clinical Significance of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Classification in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cells. 2024 Nov 19;13(22):1909. doi: 10.3390/cells13221909. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594657 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding genetic variations associated with familial breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;22(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03553-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39390525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Oct;23(6):2209-2220. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-00998-2. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36715834
-
Slit2/Robo1 signaling inhibits small-cell lung cancer by targeting β-catenin signaling in tumor cells and macrophages.Mol Oncol. 2023 May;17(5):839-856. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13289. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Mol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35838343 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Target Chemoradiotherapy Resistance in Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;16(20):3438. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203438. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

