Dietary Patterns and Their Associations With the FTO and FGF21 Gene Variants Among Emirati Adults
- PMID: 34095191
- PMCID: PMC8171665
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.668901
Dietary Patterns and Their Associations With the FTO and FGF21 Gene Variants Among Emirati Adults
Abstract
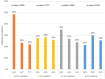
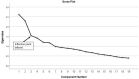
Purpose: To examine the dietary patterns and their associations with the FTO and FGF21 gene variants among Emirati adults. Methods: Using a cross-sectional design, healthy adult male and female Emiratis (n = 194) were recruited from primary health care centers in Sharjah, UAE. Participants completed a 61-item semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire. In addition, a saliva sample was obtained for the genetic analysis. Genotyping was performed for FTOrs9939609(A>T), FTOrs9930506(A>G), FGF21 rs838133 (A > G), and FGF21 rs838145 (A > G). Dietary patterns were derived using the principal component analysis. Logistic regression analyses were used to examine the association of dietary patterns with genetic variants. Results: Three dietary patterns were identified: "Western": consisting of fast food, sweets, and processed meat; "Traditional Emirati" rich in vegetables, traditional Emirati-mixed-dishes and whole dairy; while whole grains, low-fat dairy, and bulgur were components of the "Prudent" pattern. Subjects carrying the A allele of the FTO rs9939609 were 2.41 times more likely to adhere to the Western pattern compared to subjects with genotype TT (OR:2.41; 95%CI:1.05-5.50). Compared with subjects with A/A, those carrying the G allele of the FTO rs9930506 were more likely to follow a Western diet (OR: 2.19; 95%CI: 1.00-4.97). Participants carrying the risk allele (A) of the FGF21 rs838133 were twice more likely to adhere to the Traditional pattern as compared to subjects with genotype GG (OR: 1.9, 95%CI: 1.01-3.57). Conclusions: The findings of this study suggested associations among specific FTO and FGF21 gene variants with dietary patterns among Emirati adults. These findings could be used to inform evidence-based targeted nutrition preventive recommendations, especially those aiming to limit intake of western type foods.
Keywords: Emirati; FGF21 gene; FTO gene; UAE; dietary pattern; traditional diet; western diet.
Copyright © 2021 Naja, Itani, Hammoudeh, Manzoor, Abbas, Radwan and Saber-Ayad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014 (2014). Available online at: https://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-status-report-2014/en/ (accessed December 15, 2020).
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. . Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. (2014) 384:766–81. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources