Knockdown of lncRNA ENST00000609755.1 Confers Protection Against Early oxLDL-Induced Coronary Heart Disease
- PMID: 34095248
- PMCID: PMC8175657
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.650212
Knockdown of lncRNA ENST00000609755.1 Confers Protection Against Early oxLDL-Induced Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract
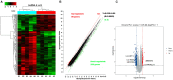
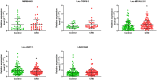
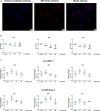
Background: This study investigated the association between long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and coronary heart disease (CHD) and further elucidated the potential biological roles of lncRNAs in CHD pathogenesis. Methods: A case-control study (590 patients and 590 controls) was conducted from February 2017 and March 2019 in Fuzhou, China. Environmental factors were investigated using questionnaires and physical examinations. Five representative lncRNAs were screened using lncRNA microarray (peripheral blood in 5 cases and 5 controls) and further verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (peripheral blood leukocyte in 100 cases and 100 controls). Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) was used to induce a human coronary artery endothelial cell (HCAECs) injury model, and loss of function was used to elucidate the role of lncRNA ENST00000609755.1 (lnc-MICALL2-2) in oxLDL-induced HCAECs injury. Results: A total of 320 lncRNAs were found dysregulated in CHD patients (fold change> 2, p < 0.05). The results of a discovery microarray, population verification and HCAEC experiments suggested the lnc-MICALL2-2 is upregulated in CHD subjects and in an oxLDL-induced HCAECs injury model. Conversely, lnc-MICALL2-2 inhibition in vitro attenuated the effects of oxLDL on HCAECs morphology, proliferation, and apoptosis. Conclusion: Elevated expression of lnc-MICALL2-2 is an independent risk factor for CHD, and knockdown subsequently confers protection against early pathological processes of oxLDL-induced CHD.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; environmental factors; human coronary artery endothelial cells; long non-coding RNA; oxidized low-density lipoprotein.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Huang, Wan, Ruan, Xie, Wei, Li, Lin, Li and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Possible causes of atherosclerosis: lncRNA COLCA1 induces oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells and impairs wound healing.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Mar;10(6):286. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-507. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35434044 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA Landscape of Coronary Atherosclerosis Reveals Differentially Expressed LncRNAs in Proliferation and Migration of Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 18;9:656636. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.656636. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34084771 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lnc-KCNC3-3:1 Alleviates the Development of Atherosclerosis via Downregulation of JAK1/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 3;8:701058. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.701058. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34540913 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary verification of lncRNA ENST00000609755.1 potential ceRNA regulatory network in coronary heart disease.Int J Cardiol. 2021 Apr 1;328:165-175. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.11.064. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Int J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33279591
-
Plasma oxidized low-density lipoprotein, a strong predictor for acute coronary heart disease events in apparently healthy, middle-aged men from the general population.Circulation. 2005 Aug 2;112(5):651-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.529297. Epub 2005 Jul 25. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 16043640
Cited by
-
Effect of berberine on global modulation of lncRNAs and mRNAs expression profiles in patients with stable coronary heart disease.BMC Genomics. 2022 May 26;23(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08641-2. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35619068 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of MicroRNAs, Long Non-Coding RNAs, and CircRNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases.Cells. 2023 Jun 14;12(12):1629. doi: 10.3390/cells12121629. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echinacoside activates Nrf2/PPARγ signaling pathway to modulate mitochondrial fusion-fission balance to ameliorate ox-LDL-induced dysfunction of coronary artery endothelial cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Dec;397(12):9767-9776. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03233-1. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38916831
References
-
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators . Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1736–88. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aggio D, Papachristou E, Papacosta O, Lennon LT, Ash S, Whincup P, et al. . Trajectories of physical activity from midlife to old age and associations with subsequent cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. J Epidemiol Commun Health. (2020) 74:130–6. 10.1136/jech-2019-212706 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pogosova N, Kotseva K, De Bacquer D, von Känel R, De Smedt D, Bruthans J, et al. . Psychosocial risk factors in relation to other cardiovascular risk factors in coronary heart disease: results from the EUROASPIRE IV survey. A registry from the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2017) 24:1371–80. 10.1177/2047487317711334 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

