Benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation in COVID-19: a prospective observational cohort study
- PMID: 34095290
- PMCID: PMC7957293
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00108-2021
Benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation in COVID-19: a prospective observational cohort study
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can result in a large variety of chronic health issues such as impaired lung function, reduced exercise performance and diminished quality of life. Our study aimed to investigate the efficacy, feasibility and safety of pulmonary rehabilitation in COVID-19 patients and to compare outcomes between patients with a mild/moderate and a severe/critical course of the disease.
Methods: Patients in the post-acute phase of a mild to critical course of COVID-19 admitted to a comprehensive 3-week inpatient pulmonary rehabilitation programme were included in this prospective, observational cohort study. Several measures of exercise performance (6-min walk distance (6MWD)), lung function (forced vital capacity (FVC)) and quality of life (36-question short-form health survey (SF-36)) were assessed before and after pulmonary rehabilitation.
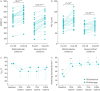
Results: 50 patients were included in the study (24 with mild/moderate and 26 with severe/critical COVID-19). On admission, patients had a reduced 6MWD (mild: median 509 m, interquartile range (IQR) 426-539 m; severe: 344 m, 244-392 m), an impaired FVC (mild: 80%, 59-91%; severe: 75%, 60-91%) and a low SF-36 mental health score (mild: 49 points, 37-54 points; severe: 39 points, 30-53 points). Patients attended a median (IQR) 100% (94-100%) of all provided pulmonary rehabilitation sessions. At discharge, patients in both subgroups improved in 6MWD (mild/moderate: +48 m, 35-113 m; severe/critical: +124 m, 75-145 m; both p<0.001), FVC (mild/moderate: +7.7%, 1.0-17.8%, p=0.002; severe/critical: +11.3%, 1.0-16.9%, p<0.001) and SF-36 mental component (mild/moderate: +5.6 points, 1.4-9.2 points, p=0.071; severe/critical: +14.4 points, -0.6-24.5, p<0.001). No adverse event was observed.
Conclusion: Our study shows that pulmonary rehabilitation is a feasible, safe and effective therapeutic option in COVID-19 patients independent of disease severity.
Copyright ©The authors 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: R. Gloeckl has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D. Leitl has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: I. Jarosch has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: T. Schneeberger has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Nell has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Stenzel has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C.F. Vogelmeier has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: K. Kenn has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.R. Koczulla has nothing to disclose.
Figures
Comment on
-
The benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with COVID-19.ERJ Open Res. 2021 May 31;7(2):00212-2021. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00212-2021. eCollection 2021 Apr. ERJ Open Res. 2021. PMID: 34084778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Clinical Management of COVID-19. May 27, 2020. Available from: www.who.int/publications/i/item/clinical-management-of-covid-19 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
