Neonatal hemoglobin affects the accuracy of whole blood bilirubin measurement on GEM Premier 4000 blood gas analyzers
- PMID: 34095416
- PMCID: PMC8145737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plabm.2021.e00231
Neonatal hemoglobin affects the accuracy of whole blood bilirubin measurement on GEM Premier 4000 blood gas analyzers
Abstract
Objectives: Whole blood bilirubin measured on blood gas analyzers is accepted by physicians in neonatal hyperbilirubinemia management since it requires a small sample volume. The accuracy of bilirubin measurement on blood gas analyzers is instrument dependent and remains controversial.
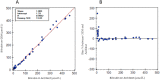
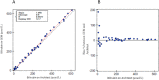
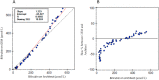
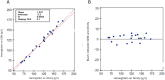
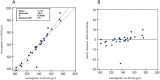
Design and methods: Bilirubin in adult and umbilical cord whole blood samples, spiked with an unconjugated bilirubin standard, and non-spiked adult plasma samples was measured on a blood gas analyzer (GEM 4000) and a Core Laboratory Chemistry analyzer (Architect c16000) respectively. We also investigated the linear regression for neonatal and adult hemoglobin measured on the blood gas analyzer and the Core Laboratory hematology analyzer (Alinity h-Series).
Results: Plasma bilirubin measured on the blood gas analyzer and the chemistry analyzer was statistically identical. Adult whole blood bilirubin showed slightly increased proportional bias. When umbilical cord whole blood samples were used, the Deming regression showed GEM bilirubin =1.233(Architect) (95% CI 1.199 ~ 1.266)-44.43 μmol/L (95% CI -53.6 ~ -35.2). The regression was significantly different from that in plasma (p < 0.001) or adult whole blood (p < 0.001) samples. 36.1% neonatal samples with bilirubin levels >50 μmol/L showed that the bias% was above laboratory standards. In addition, the regression of neonatal hemoglobin measurement between the GEM and the Alinity was significantly different from adult hemoglobin (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: Neonatal whole blood bilirubin measurement on blood gas analyzers may be affected by neonatal hemoglobin. The method should be validated using neonatal whole blood samples or samples with a similar matrix before the analyzers are implemented into neonatal hyperbilirubinemia management.
Keywords: Hyperbilirubinemia and blood gas analyzer; Neonates; Whole blood bilirubin.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limitations and opportunities of whole blood bilirubin measurements by GEM premier 4000®.BMC Pediatr. 2017 Mar 29;17(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0842-8. BMC Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28356083 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical performance validation and clinical application of blood gas analyzer on the detection of neonatal bilirubin.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Dec;10(12):3175-3183. doi: 10.21037/tp-21-541. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 35070831 Free PMC article.
-
Novel In-Line Hemolysis Detection on a Blood Gas Analyzer and Impact on Whole Blood Potassium Results.Clin Chem. 2024 Dec 2;70(12):1485-1493. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvae135. Clin Chem. 2024. PMID: 39293997
-
Prevention of bilirubin encephalopathy.Biol Neonate. 2001;79(3-4):219-23. doi: 10.1159/000047095. Biol Neonate. 2001. PMID: 11275655 Review.
-
Diagnostic methods for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: benefits, limitations, requirements, and novel developments.Pediatr Res. 2021 Aug;90(2):277-283. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01546-y. Epub 2021 May 4. Pediatr Res. 2021. PMID: 33948000 Review.
Cited by
-
Accuracy and Reliability of Whole Blood Bilirubin Measurements Using a Roche Blood Gas Analyzer for Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia Screening and Risk Stratification.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jul 4;10:910566. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.910566. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35859945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhutani V.K., Johnson L., Sivieri E.M. Predictive ability of a predischarge hour-specific serum bilirubin for subsequent significant hyperbilirubinemia in healthy term and near-term newborns. Pediatrics. 1999 Jan;103(1):6–14. - PubMed
-
- Linderkamp O., Nash G.B., Wu P.Y., Meiselman H.J. Deformability and intrinsic material properties of neonatal red blood cells. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1244–1250. - PubMed
-
- Rochette J., Craig J.E., Thein S.L. Fetal hemoglobin levels in adults. Blood Rev. 1994 Dec;8(4):213–224. - PubMed
-
- Peake M., Mazzachi B., Fudge A., Bais R. Bilirubin measured on a blood gas analyser: a suitable alternative for near-patient assessment of neonatal Jaundice? Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2001 Sep;38(Pt 5):533–540. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

