19-hydroxy Steroids in the Aromatase Reaction: Review on Expression and Potential Functions
- PMID: 34095690
- PMCID: PMC8169043
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvab050
19-hydroxy Steroids in the Aromatase Reaction: Review on Expression and Potential Functions
Abstract
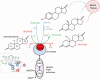
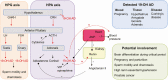
Scientific evidence related to the aromatase reaction in various biological processes spanning from mid-1960 to today is abundant; however, as our analytical sensitivity increases, a new look at the old chemical reaction is necessary. Here, we review an irreversible aromatase reaction from the substrate androstenedione. It proceeds in 3 consecutive steps. In the first 2 steps, 19-hydroxy steroids are produced. In the third step, estrone is produced. They can dissociate from the enzyme complex and either accumulate in tissues or enter the blood. In this review, we want to highlight the potential importance of these 19-hydroxy steroids in various physiological and pathological conditions. We focus primarily on 19-hydroxy steroids, and in particular on the 19-hydroxyandrostenedione produced by the incomplete aromatase reaction. Using a PubMed database and the search term "aromatase reaction," 19-hydroxylation of androgens and steroid measurements, we detail the chemistry of the aromatase reaction and list previous and current methods used to measure 19-hydroxy steroids. We present evidence of the existence of 19-hydroxy steroids in brain tissue, ovaries, testes, adrenal glands, prostate cancer, as well as during pregnancy and parturition and in Cushing's disease. Based on the available literature, a potential involvement of 19-hydroxy steroids in the brain differentiation process, sperm motility, ovarian function, and hypertension is suggested and warrants future research. We hope that with the advancement of highly specific and sensitive analytical methods, future research into 19-hydroxy steroids will be encouraged, as much remains to be learned and discovered.
Keywords: 19-hydroxyandrostenedione; 19-oxoandrostenedione; ACTH; HPA and HPG axes; POR.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aromatase and nonaromatizing 10-demethylase activity of adrenal cortex mitochondrial P-450(11)beta.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):31-7. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90004-5. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988. PMID: 3264134
-
Profiling adrenal 11β-hydroxyandrostenedione metabolites in prostate cancer cells, tissue and plasma: UPC2-MS/MS quantification of 11β-hydroxytestosterone, 11keto-testosterone and 11keto-dihydrotestosterone.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Feb;166:54-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.06.009. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27345701
-
Pathways and genes involved in steroid hormone metabolism in male pigs: a review and update.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Mar;140:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24239507 Review.
-
P-450(11beta)-dependent conversion of androgen to estrogen, the aromatase reaction.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):530-5. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90764-3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986. PMID: 3490848
-
Metabolism of 19-methyl substituted steroids and a proposal for the third aromatase monooxygenation.Steroids. 1987 Oct-Dec;50(4-6):363-74. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(87)90025-0. Steroids. 1987. PMID: 3332933 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilisation of the Innovative [18F]-Labelled Radiotracer [18F]-BIBD-071 Within HR+ Breast Cancer Xenograft Mouse Models.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;18(1):66. doi: 10.3390/ph18010066. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861129 Free PMC article.
-
Sex steroid hormone synthesis, metabolism, and the effects on the mammalian olfactory system.Cell Tissue Res. 2023 Jan;391(1):19-42. doi: 10.1007/s00441-022-03707-9. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Cell Tissue Res. 2023. PMID: 36401093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shen AL, O’Leary KA, Kasper CB. Association of multiple developmental defects and embryonic lethality with loss of microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(8):6536–6541. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
