High resolution RNA-seq profiling of genes encoding ribosomal proteins across different organs and developmental stages in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 34095740
- PMCID: PMC8156134
- DOI: 10.1002/pld3.320
High resolution RNA-seq profiling of genes encoding ribosomal proteins across different organs and developmental stages in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
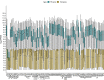
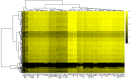
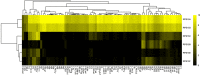
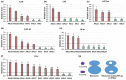
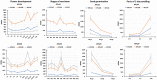
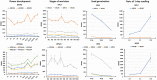
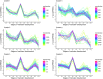
In Arabidopsis thaliana, each ribosomal protein (RP) is encoded by a small gene family consisting of two or more highly homologous paralogues, which results in ribosome heterogeneity. It is largely unknown that how genes from multiple member containing RP families are regulated at transcriptional level to accommodate the needs of different plant organs and developmental stages. In this study, we investigated the transcript accumulation profiles of RP genes and found that the expression levels of RP genes are varied dramatically in different organs and developmental stages. Although most RP genes are found to be ubiquitously transcribed, some are obviously transcribed with spatiotemporal specificity. The hierarchical clustering trees of transcript accumulation intensity of RP genes revealed that different organs and developmental stages have different population of RP gene transcripts. By interrogating of the expression fluctuation trend of RP genes, we found that in spite of the fact that most groups of paralogous RP genes are transcribed in concerted manners, some RPs gene have contrasting expression patterns. When transcripts of paralogous RP genes from the same family are considered together, the expression level of most RP genes are well-matched but some are obviously higher or lower, therefore we speculate that some superfluous RPs may act outside the ribosome and a portion of ribosomes may lack one or even more RP(s). Altogether, our analysis results suggested that functional divergence may exist among heterogeneous ribosomes that resulted from different combination of RP paralogues, and substoichiometry of several RP gene families may lead to another layer of heterogeneous ribosomes which also have divergent functions in plants.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; functional specialization; gene duplication; paralogue; ribosomal protein; ribosome heterogeneity; transcript profiling.
© 2021 The Authors. Plant Direct published by American Society of Plant Biologists, Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression changes of ribosomal proteins in phosphate- and iron-deficient Arabidopsis roots predict stress-specific alterations in ribosome composition.BMC Genomics. 2013 Nov 13;14:783. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-783. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24225185 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis paralogous genes RPL23aA and RPL23aB encode functionally equivalent proteins.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Oct 8;20(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02672-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33032526 Free PMC article.
-
Differential transcript accumulation and subcellular localization of Arabidopsis ribosomal proteins.Plant Sci. 2014 Jun;223:134-45. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.03.011. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24767123
-
Systematic Review of Plant Ribosome Heterogeneity and Specialization.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jun 25;11:948. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00948. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32670337 Free PMC article.
-
Extraribosomal Functions of Cytosolic Ribosomal Proteins in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Apr 21;12:607157. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.607157. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33968093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games.Cells. 2025 Mar 21;14(7):473. doi: 10.3390/cells14070473. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remodelled ribosomal populations synthesize a specific proteome in proliferating plant tissue during cold.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 Mar 6;380(1921):20230384. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0384. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40045790 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Adaptive Regulation of the Leaf-Petiole System: Strategies for Survival of Water Lily Plants under Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 15;24(6):5605. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065605. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982679 Free PMC article.
-
Mining the Candidate Transcription Factors Modulating Tanshinones' and Phenolic Acids' Biosynthesis Under Low Nitrogen Stress in Salvia miltiorrhiza.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 19;26(4):1774. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041774. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, K. L. , Cronn, R. , Percifield, R. , & Wendel, J. F. (2003). Genes duplicated by polyploidy show unequal contributions to the transcriptome and organ‐specific reciprocal silencing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 4649–4654. 10.1073/pnas.0630618100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armache, J.‐P. , Jarasch, A. , Anger, A. M. , Villa, E. , Becker, T. , Bhushan, S. , Jossinet, F. , Habeck, M. , Dindar, G. , Franckenberg, S. , Marquez, V. , Mielke, T. , Thomm, M. , Berninghausen, O. , Beatrix, B. , Söding, J. , Westhof, E. , Wilson, D. N. , & Beckmann, R. (2010). Localization of eukaryote‐specific ribosomal proteins in a 5.5‐Å cryo‐EM map of the 80S eukaryotic ribosome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 19754–19759. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian, S. , Zheng, D. , Liu, Y. J. , Fang, G. , Frankish, A. , Carriero, N. , Robilotto, R. , Cayting, P. , & Gerstein, M. (2009). Comparative analysis of processed ribosomal protein pseudogenes in four mammalian genomes. Genome Biology, 10, R2. 10.1186/gb-2009-10-1-r2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

