Explainable AI and Reinforcement Learning-A Systematic Review of Current Approaches and Trends
- PMID: 34095817
- PMCID: PMC8172805
- DOI: 10.3389/frai.2021.550030
Explainable AI and Reinforcement Learning-A Systematic Review of Current Approaches and Trends
Abstract
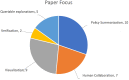
Research into Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has been increasing in recent years as a response to the need for increased transparency and trust in AI. This is particularly important as AI is used in sensitive domains with societal, ethical, and safety implications. Work in XAI has primarily focused on Machine Learning (ML) for classification, decision, or action, with detailed systematic reviews already undertaken. This review looks to explore current approaches and limitations for XAI in the area of Reinforcement Learning (RL). From 520 search results, 25 studies (including 5 snowball sampled) are reviewed, highlighting visualization, query-based explanations, policy summarization, human-in-the-loop collaboration, and verification as trends in this area. Limitations in the studies are presented, particularly a lack of user studies, and the prevalence of toy-examples and difficulties providing understandable explanations. Areas for future study are identified, including immersive visualization, and symbolic representation.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; explainable AI; machine learning; reinforcement learning; visualization.
Copyright © 2021 Wells and Bednarz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Adebayo J., Gilmer J., Muelly M., Goodfellow I., Hardt M., Kim B. (2018). Sanity checks for saliency maps. arXiv [Preprint] arXiv:1810.03292.
-
- Anjomshoae S., Najjar A., Calvaresi D., Främling K. (2019). Explainable agents and robots: results from a systematic literature review, in 18th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2019), Montreal, Canada, May 13–17, 2019 (Montreal, QC: International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems; ), 1078–1088.
-
- Araiza-Illan D., Eder K. (2019). Safe and trustworthy human-robot interaction, in Humanoid Robotics: A Reference, eds Goswami A., Vadakkepat P. (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands; ), 2397–2419.
-
- Baker B., Kanitscheider I., Markov T., Wu Y., Powell G., McGrew B., et al. . (2019). Emergent tool use from multi-agent autocurricula. arXiv [Preprint] arXiv:1909.07528.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

