On the intrinsic reactivity of highly potent trypanocidal cruzain inhibitors
- PMID: 34095840
- PMCID: PMC8126975
- DOI: 10.1039/d0md00097c
On the intrinsic reactivity of highly potent trypanocidal cruzain inhibitors
Abstract
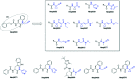
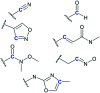
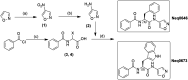
The cysteine protease cruzipain is considered to be a validated target for therapeutic intervention in the treatment of Chagas disease. Hence, peptidomimetic cruzipain inhibitors having a reactive group (known as warhead) are subject to continuous studies to discover novel antichagasic compounds. Here, we evaluated how different warheads for a set of structurally similar related compounds could inhibit the activity of cruzipain and, ultimately, their trypanocidal effect. We first investigated in silico the intrinsic reactivity of these compounds by applying the Fukui index to correlate it with the enzymatic affinity. Then, we evaluated their potency against T. cruzi (Y and Tulahuen strains), which revealed the reversible cruzain inhibitor Neq0656 as a better trypanocidal agent (ECY.strain 50 = 0.1 μM; SI = 58.4) than the current drug benznidazole (ECY.strain 50 = 5.1 μM; SI > 19.6). We also measured the half-life time by HPLC analysis of three lead compounds in the presence of glutathione and cysteine to experimentally assess their intrinsic reactivity. Results clearly illustrated the reactivity trend for the warheads (azanitrile > aldehyde > nitrile), where the aldehyde displayed an intermediate intrinsic reactivity. Therefore, the aldehyde bearing peptidomimetic compounds should be subject for in-depth evaluation in the drug discovery process.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure-Based and Molecular Modeling Studies for the Discovery of Cyclic Imides as Reversible Cruzain Inhibitors With Potent Anti-Trypanosoma cruzi Activity.Front Chem. 2019 Nov 25;7:798. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00798. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31824926 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular design aided by random forests and synthesis of potent trypanocidal agents as cruzain inhibitors for Chagas disease treatment.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2020 Sep;96(3):948-960. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13663. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2020. PMID: 33058457
-
Structural design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of thiazoles against Trypanosoma cruzi.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Dec 1;141:346-361. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.047. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 29031078
-
Reversible and non-covalent benzimidazole-based in vivo lead for Chagas disease.2011 Apr 15 [updated 2013 Feb 28]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2011 Apr 15 [updated 2013 Feb 28]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 23658943 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
[The chemotherapy of Chagas disease].Medicina (B Aires). 1999;59 Suppl 2:147-65. Medicina (B Aires). 1999. PMID: 10668258 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Nitriles: an attractive approach to the development of covalent inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Nov 7;14(2):201-217. doi: 10.1039/d2md00204c. eCollection 2023 Feb 22. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36846367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Masked Aldehyde Inhibitors: A Novel Strategy for Inhibiting Cysteine Proteases.J Med Chem. 2021 Aug 12;64(15):11267-11287. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00628. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34288674 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

