New insights into ethionamide metabolism: influence of oxidized methionine on its degradation path
- PMID: 34095849
- PMCID: PMC8126880
- DOI: 10.1039/d0md00253d
New insights into ethionamide metabolism: influence of oxidized methionine on its degradation path
Abstract
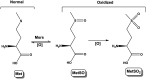
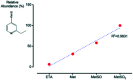
Ethionamide (ETH) is a commercial drug, used as a second-line resource to neutralize Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. It is proven that its metabolization in the organism leads to the formation of the active form of the drug, but some metabolic pathways may lead to the loss of its activity. Our work proved that the presence of oxidized methionine in cells could influence ETH's degradation, leading to the appearance of an inactive metabolite that is detectable by HPLC and mass spectrometry. In addition, it was found this process increases with the degree of methionine oxidation. This study contributes to a better understanding of ethionamide's metabolism in living organisms, and can help in the design of new drugs or ethionamide boosters for the combat of multidrug resistant tuberculosis.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
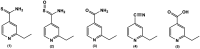

Similar articles
-
Ethionamide biomimetic activation and an unprecedented mechanism for its conversion into active and non-active metabolites.Org Biomol Chem. 2016 Sep 21;14(37):8848-8858. doi: 10.1039/c6ob01561a. Org Biomol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27714216
-
Preparation and biological evaluation of ethionamide-mesoporous silicon nanoparticles against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Feb 1;27(3):403-405. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.12.060. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28057421
-
How a PCR Sequencing Strategy Can Bring New Data to Improve the Diagnosis of Ethionamide Resistance.Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 15;10(7):1436. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071436. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889155 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of the antituberculosis drug ethionamide.Curr Drug Metab. 2013 Jan;14(1):151-8. Curr Drug Metab. 2013. PMID: 23215813 Review.
-
Resistance to Isoniazid and Ethionamide in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Genes, Mutations, and Causalities.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Aug;2(4):MGM2-0014-2013. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MGM2-0014-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Biochemical Advances in Antitubercular Drugs: Challenges and Future.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(21):1829-1855. doi: 10.2174/0115680266286294240610102911. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38919089 Review.
References
-
- Siegel R. L. Miller K. D. Jemal A. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Bastian I. Colebunders R. Drugs. 1999;58:633–661. - PubMed
-
- Hait W. N. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2010;9:253. - PubMed
-
- Vale N. Correia A. Silva S. Figueiredo P. Mäkilä E. Salonen J. Hirvonen J. Pedrosa J. Santos H. A. Fraga A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017;27:403–405. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

