An optimized protocol for isolation of S-nitrosylated proteins from C. elegans
- PMID: 34095861
- PMCID: PMC8164088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100547
An optimized protocol for isolation of S-nitrosylated proteins from C. elegans
Abstract
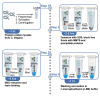
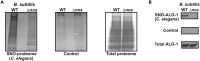
Post-translational modification by S-nitrosylation regulates numerous cellular functions and impacts most proteins across phylogeny. We describe a protocol for isolating S-nitrosylated proteins (SNO-proteins) from C. elegans, suitable for assessing SNO levels of individual proteins and of the global proteome. This protocol features efficient nematode lysis and SNO capture, while protection of SNO proteins from degradation is the major challenge. This protocol can be adapted to mammalian tissues. For complete information on the generation and use of this protocol, please refer to Seth et al. (2019).
Keywords: Model Organisms; Protein Biochemistry; Proteomics.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jonathan Stamler is a co-founder of the company SNO bio, which develops SNO-based therapeutics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A metabolic labeling protocol to enrich myristoylated proteins from Caenorhabditis elegans.STAR Protoc. 2021 Dec 9;2(4):101013. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.101013. eCollection 2021 Dec 17. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34917984 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol for preparing Thiopropyl Sepharose resin used for capturing S-nitrosylated proteins.STAR Protoc. 2023 Dec 15;4(4):102430. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102430. Epub 2023 Nov 4. STAR Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37925633 Free PMC article.
-
A worm rich in protein: Quantitative, differential, and global proteomics in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Proteomics. 2010 Oct 10;73(11):2186-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2010.03.014. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20398808 Review.
-
NeuCode Labeling in Nematodes: Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Impact of Ascaroside Treatment in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015 Nov;14(11):2922-35. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.049684. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 26392051 Free PMC article.
-
Solid-phase capture for the detection and relative quantification of S-nitrosoproteins by mass spectrometry.Methods. 2013 Aug 1;62(2):130-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Methods. 2013. PMID: 23064468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An NRF2/β3-Adrenoreceptor Axis Drives a Sustained Antioxidant and Metabolic Rewiring Through the Pentose-Phosphate Pathway to Alleviate Cardiac Stress.Circulation. 2025 May 6;151(18):1312-1328. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.067876. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Circulation. 2025. PMID: 40071326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adak S., Aulak K.S., Stuehr D.J. Direct evidence for nitric oxide production by a nitric-oxide synthase-like protein from Bacillus subtilis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:16167–16171. - PubMed
-
- Chung H.S., Murray C.I., Venkatraman V., Crowgey E.L., Rainer P.P., Cole R.N., Bomgarden R.D., Rogers J.C., Balkan W., Hare J.M. Dual labeling biotin switch assay to reduce bias derived from different cysteine subpopulations: a method to maximize S-nitrosylation detection. Circ. Res. 2015;117:846–857. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forrester M.T., Foster M.W., Stamler J.S. Assessment and application of the biotin switch technique for examining protein S-nitrosylation under conditions of pharmacologically induced oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:13977–13983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

