Protocol for genome-scale CRISPR screening in engineered lineage reporter hPSCs to study cell fate determination
- PMID: 34095862
- PMCID: PMC8164093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100548
Protocol for genome-scale CRISPR screening in engineered lineage reporter hPSCs to study cell fate determination
Abstract
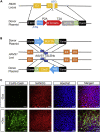
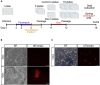
PAX6 is a key determinant of human neuroectoderm cell fate. Here, we describe a protocol for genome-scale CRISPR screening for use in genetically engineered human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). Using the germ layer reporter PAX6 and an inducible CRISPR/Cas9 knockout system, we describe how to identify lineage-specific preventing genes. This protocol can be applied for use with other reporter genes to study cell fate determination in hPSCs. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Xu et al. (2021).
Keywords: CRISPR; Cell Differentiation; High Throughput Screening; Stem Cells.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protocol for the Generation of Human Pluripotent Reporter Cell Lines Using CRISPR/Cas9.STAR Protoc. 2020 Sep 18;1(2):100052. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2020.100052. Epub 2020 Jun 13. STAR Protoc. 2020. PMID: 33073252 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Editing to Generate Versatile Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Reporter Lines for Analysis of Differentiation and Lineage Tracing.Stem Cells. 2019 Dec;37(12):1556-1566. doi: 10.1002/stem.3096. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 31634414
-
A Method to Map Gene Essentiality of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells by Genome-Scale CRISPR Screens with Inducible Cas9.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2377:1-27. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1720-5_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34709608 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in human pluripotent stem cells: Harnessing human genetics in a dish.Dev Dyn. 2016 Jul;245(7):788-806. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24414. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Dev Dyn. 2016. PMID: 27145095 Review.
-
Controlling transcription in human pluripotent stem cells using CRISPR-effectors.Methods. 2016 May 15;101:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Methods. 2016. PMID: 26525193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of label-free light-controlled gene expression technologies using mid-IR and terahertz light.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 11;12:1324757. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1324757. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39465004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chi L., Fan B., Feng D., Chen Z., Liu Z., Hui Y., Xu X., Ma L., Fang Y., Zhang Q. The dorsoventral patterning of human forebrain follows an activation/transformation model. Cereb. Cortex. 2017;27:2941–2954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

