A prospective study comparing rectal water contrast-transvaginal ultrasonography with sonovaginography for the diagnosis of deep posterior endometriosis
- PMID: 34096037
- PMCID: PMC8457128
- DOI: 10.1111/aogs.14209
A prospective study comparing rectal water contrast-transvaginal ultrasonography with sonovaginography for the diagnosis of deep posterior endometriosis
Abstract
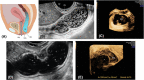
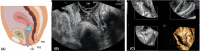
Introduction: Preoperative assessment of deep endometriotic (DE) nodules is necessary to inform patients about the possible treatments and provide informed consent in case of surgery. This study aims to investigate the diagnostic performance of rectal water-contrast transvaginal ultrasonography (RWC-TVS) and sonovaginography (SVG) in women with suspicion of posterior DE.
Material and methods: This prospective comparative study (NCT04296760) enrolled women with clinical suspicion of DE at our institution (Piazza della Vittoria 14 SRL, Genoa, Italy). Exclusion criteria were previous diagnosis of DE by imaging techniques or laparoscopy. All patients underwent RWC-TVS and SVG, independently performed by two gynecological sonologists blinded to the other technique's results. Patients underwent laparoscopic surgery within the following three months; imaging findings were compared with surgical and histological results.
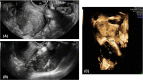
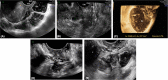
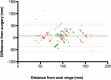
Results: In 208 of 281 (74.0%) patients included, posterior DE was surgically confirmed in rectosigmoid (n = 88), vagina (n = 21), rectovaginal septum (n = 34) and uterosacral ligaments (n = 156). RWC-TVS and SVG demonstrated similar sensitivity (SE; 93.8% vs 89.4%; p = 0.210) and specificity (SP; 86.3% vs 79.4%; p = 0.481) in diagnosing posterior DE. Specifically, both examinations had similar accuracy in detecting nodules of uterosacral ligaments (p = 0.779), vagina (p = 0.688) and rectovaginal septum (p = 0.824). RWC-TVS had higher SE (95.2% vs 82.0%; p = 0.003) and similar SP (99.5% vs 98.5%; p = 0.500) in diagnosing rectosigmoid endometriosis and estimated better infiltration of intestinal submucosa (p = 0.039), and distance between these nodules and anal verge (p < 0.001); only RWC-TVS allowed the estimation of bowel lumen stenosis. A similar proportion of discomfort was experienced during both examinations (p = 0.191), although a statistically higher mean visual analog score was reported during RWC-TVS (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Although RWC-TVS and SVG have similar accuracy in the diagnosis of DE, RWC-TVS performed better in assessment of the characteristics of rectosigmoid endometriosis.
Keywords: enhanced transvaginal ultrasound; posterior compartment deep endometriosis; rectal water contrast transvaginal ultrasonography; rectosigmoid endometriosis; sonovaginography.
© 2021 The Authors. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology (NFOG).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Koninckx PR, Ussia A, Adamyan L, Wattiez A, Donnez J. Deep endometriosis: definition, diagnosis, and treatment. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:564‐571. - PubMed
-
- Bazot M, Darai E. Diagnosis of deep endometriosis: clinical examination, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, and other techniques. Fertil Steril. 2017;108:886‐894. - PubMed
-
- Chapron C, Dubuisson JB, Pansini V, et al. Routine clinical examination is not sufficient for diagnosing and locating deeply infiltrating endometriosis. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2002;9:115‐119. - PubMed
-
- Donnez O, Roman H. Choosing the right surgical technique for deep endometriosis: shaving, disc excision, or bowel resection? Fertil Steril. 2017;108:931‐942. - PubMed
-
- Berlanda N, Somigliana E, Frattaruolo MP, Buggio L, Dridi D, Vercellini P. Surgery versus hormonal therapy for deep endometriosis: is it a choice of the physician? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017;209:67‐71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

