Xeno-Free Human Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Maintain Their Characteristic Properties after Long-Term Cryopreservation
- PMID: 34096215
- PMCID: PMC8181313
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2021.7131
Xeno-Free Human Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Maintain Their Characteristic Properties after Long-Term Cryopreservation
Abstract
Objective: The past decade has witnessed a rapid growth in harnessing the potential of adult stem cells for regenerative medicine. An investigational new drug (IND) or a regenerative medicine advanced therapy (RMAT) product must fulfil many requirements, such as stability studies, after cryopreservation. Such studies are important to ascertain the utility of off-the-shelf allogeneic cells for clinical applications. The present work describes a complete characterisation of xenofree human Wharton's Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells (hWJ-MSCs) before and up to 28 months post-cryopreservation.
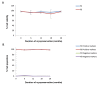
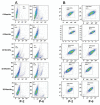
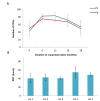
Materials and methods: In this experimental study, culture methods that involved plasma derived human serum and recombinant trypsin were used to develop clinical grade cells. Complete cell characterisation involved flow cytometry studies for viability, positive and negative markers, colony forming unit (CFU) potential, population doubling time (PDT), soft agar assay to evaluate in vitro tumourigenicity, karyotype analysis and differentiation studies which were performed before and at 6, 12, 18 and 28 months post-cryopreservation.
Results: Our data showed consistency in the flow cytometry, CFU assay, PDT, soft agar assay, karyotyping and differentiation studies.
Conclusion: Using our protocols for extended xeno-free culture and cryopreservation of hWJ-MSCs, we could establish the shelf life of the cell-based product for up to 28 months.
Keywords: Mesenchymal Stromal Cells; Stability; Umbilical Cord; Wharton’s Jelly.
Copyright© by Royan Institute. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isolation and Characterization of Feline Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Vet Sci. 2021 Feb 7;8(2):24. doi: 10.3390/vetsci8020024. Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33562192 Free PMC article.
-
Are serum-free and xeno-free culture conditions ideal for large scale clinical grade expansion of Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells? A comparative study.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Jul 28;5(4):88. doi: 10.1186/scrt477. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25069491 Free PMC article.
-
A xeno-free culture method that enhances Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stromal cell culture efficiency over traditional animal serum-supplemented cultures.Cytotherapy. 2014 May;16(5):683-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.07.012. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Cytotherapy. 2014. PMID: 24119645
-
Wharton's jelly-derived stromal cells and their cell therapy applications in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Mar;26(5):1339-1350. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17105. Epub 2022 Jan 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35088933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wharton's Jelly stem cells: future clinical applications.Placenta. 2011 Oct;32 Suppl 4:S311-5. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.06.010. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Placenta. 2011. PMID: 21733573 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing the growth kinetics and characteristics of Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells expanded using different culture mediums.Cytotechnology. 2025 Feb;77(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00682-7. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Cytotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39711971
References
-
- Owen M, Friedenstein AJ. Stromal stem cells: marrow-derived osteogenic precursors. Ciba Found Symp. 1988;136:42–60. - PubMed
-
- McElreavey KD, Irvine AI, Ennis KT, McLean WH. Isolation, culture and characterisation of fibroblast-like cells derived from the Wharton’s jelly portion of human umbilical cord. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991;19(1):29S–29S. - PubMed
-
- Koliakos I, Tsagias N, Karagiannis V. Mesenchymal cells isolation from Wharton’s jelly, in perspective to clinical applications. J Bio Res-Thessaloniki. 2011;16:194–201.
-
- Christodoulou I, Kolisis FN, Papaevangeliou D, Zoumpourlis V. Comparative evaluation of human mesenchymal stem cells of fetal (Wharton’s Jelly) and Adult (adipose tissue) origin during prolonged in vitro expansion: Considerations for Cytotherapy. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:246134–246134. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
