MiR-27a-3p enhances the cisplatin sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 34096570
- PMCID: PMC8661504
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20192007
MiR-27a-3p enhances the cisplatin sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt pathway
Abstract
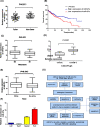
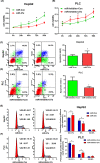
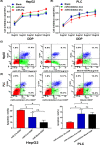
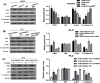
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in drug resistance, and it is reported that miR-27a-3p regulated the sensitivity of cisplatin in breast cancer, lung cancer and ovarian cancer. However, the relationship between miR-27a-3p and chemosensitivity of cisplatin in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was unclear, especially the underlying mechanism was unknown. In the present study, we analyzed miR-27a-3p expression levels in 372 tumor tissues and 49 adjacent tissues in HCC samples from TCGA database, and found that the miR-27a-3p was down-regulated in HCC tissues. The level of miR-27a-3p was associated with metastasis, Child-Pugh grade and race. MiR-27a-3p was regarded as a favorable prognosis indicator for HCC patients. Then, miR-27a-3p was overexpressed in HepG2 cell, and was knocked down in PLC cell. Next, we conducted a series of in vitro assays, including MTT, apoptosis and cell cycle assays to observe the biological changes. Further, inhibitor rate and apoptosis rate were detected with pre- and post-cisplatin treatment in HCC. The results showed that overexpression of miR-27a-3p repressed the cell viability, promoted apoptosis and increased the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase. Importantly, overexpression of miR-27a-3p significantly increased the inhibitor rate and apoptosis rate with cisplatin intervention. Besides, we found that miR-27a-3p added cisplatin sensitivity potentially through regulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Taken together, miR-27a-3p acted as a tumor suppressor gene in HCC cells, and it could be useful for modulating cisplatin sensitivity in chemotherapy.
Keywords: Cisplatin; Hepatocellular cancer; PI3K/Akt pathway; Sensitivity; miR-27a-3p.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-128-3p overexpression sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib induced apoptosis through regulating DJ-1.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Oct;22(20):6667-6677. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201810_16143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30402839
-
MicroRNA-27a-3p inhibits cell viability and migration through down-regulating DUSP16 in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jul;119(7):5143-5152. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26526. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29143999
-
Midazolam inhibits proliferation and accelerates apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by elevating microRNA-124-3p and suppressing PIM-1.IUBMB Life. 2020 Mar;72(3):452-464. doi: 10.1002/iub.2171. Epub 2019 Oct 25. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 31651086
-
Natural Products as Modulators of miRNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Therapeutic Perspective.J Gene Med. 2025 May;27(5):e70019. doi: 10.1002/jgm.70019. J Gene Med. 2025. PMID: 40296860 Review.
-
miR-203a-A multifaceted regulator modulating cancer hallmarks and therapy response.IUBMB Life. 2024 Mar;76(3):108-124. doi: 10.1002/iub.2786. Epub 2023 Oct 4. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 37792370 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effects of thalidomide and cisplatin are mediated via the PI3K/AKT and JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathways in cervical cancer.Oncol Rep. 2022 Oct;48(4):169. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8384. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35920185 Free PMC article.
-
Role of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes in cancer drug resistance via noncoding RNAs.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 12;16(1):741. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02195-x. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40355722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA-214-3p stimulates carcinogen-induced mammary epithelial cell apoptosis in mammary cancer-resistant species.Commun Biol. 2023 Oct 3;6(1):1006. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05370-4. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37789172 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering STAT3 signaling potential in hepatocellular carcinoma: tumorigenesis, treatment resistance, and pharmacological significance.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Apr 21;28(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00438-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37085753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycyrrhizin enhances the antitumor activity of cisplatin in non‑small cell lung cancer cells by influencing DNA damage and apoptosis.Oncol Lett. 2025 Mar 4;29(4):207. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14954. eCollection 2025 Apr. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40070780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

