CRISPR/Cas13d-mediated efficient KDM5B mRNA knockdown in porcine somatic cells and parthenogenetic embryos
- PMID: 34096883
- PMCID: PMC8284906
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-21-0053
CRISPR/Cas13d-mediated efficient KDM5B mRNA knockdown in porcine somatic cells and parthenogenetic embryos
Abstract
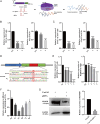
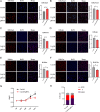
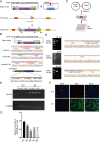
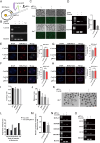
An efficient mRNA knockdown strategy is needed to explore gene function in cells and embryos, especially to understand the process of maternal mRNA decay during early embryo development. Cas13, a novel RNA-targeting CRISPR effector protein, could bind and cleave complementary single-strand RNA, which has been employed for mRNA knockdown in mouse and human cells and RNA-virus interference in plants. Cas13 has not yet been reported to be used in pigs. In the current study, we explored the feasibility of CRISPR/Cas13d-mediated endogenous RNA knockdown in pigs. KDM5B, a histone demethylase of H3K4me3, was downregulated at the transcriptional level by 50% with CRISPR/Cas13d in porcine fibroblast cells. Knockdown of KDM5B-induced H3K4me3 expression and decreased the abundance of H3K27me3, H3K9me3, H3K4ac, H4K8ac, and H4K12ac. These changes affected cell proliferation and cell cycle. Furthermore, stable integration of the CRISPR/Cas13d system into the porcine genome resulted in the continuous expression of Cas13d and persistent knockdown of KDM5B. Finally, the RNA-targeting potential of Cas13d was further validated in porcine parthenogenetic embryos. By microinjection of Cas13d mRNA and gRNA targeting KDM5B into porcine oocytes, the expression of KDM5B was downregulated, the abundance of H3K4me3 increased as expected, and the expression of embryonic development-related genes was changed accordingly. These results indicate that CRISPR/Cas13d provides an easily programmable platform for spatiotemporal transcriptional manipulation in pigs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Albert M, Schmitz SU, Kooistra SM, Malatesta M, Morales Torres C, Rekling JC, Johansen JV, Abarrategui I, Helin K. 2013. The histone demethylase Jarid1b ensures faithful mouse development by protecting developmental genes from aberrant H3K4me3. PLoS Genetics 9 e1003461. ( 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003461) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

