Zoonotic spillover: Understanding basic aspects for better prevention
- PMID: 34096963
- PMCID: PMC8182890
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2020-0355
Zoonotic spillover: Understanding basic aspects for better prevention
Abstract
The transmission of pathogens from wild animals to humans is called "zoonotic spillover". Most human infectious diseases (60-75%) are derived from pathogens that originally circulated in non-human animal species. This demonstrates that spillover has a fundamental role in the emergence of new human infectious diseases. Understanding the factors that facilitate the transmission of pathogens from wild animals to humans is essential to establish strategies focused on the reduction of the frequency of spillover events. In this context, this article describes the basic aspects of zoonotic spillover and the main factors involved in spillover events, considering the role of the inter-species interactions, phylogenetic distance between host species, environmental drivers, and specific characteristics of the pathogens, animals, and humans. As an example, the factors involved in the emergence of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic are discussed, indicating what can be learned from this public health emergency, and what can be applied to the Brazilian scenario. Finally, this article discusses actions to prevent or reduce the frequency of zoonotic spillover events.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


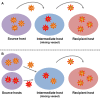

References
-
- Abreu FVS, Ribeiro IP, Ferreira-de-Brito A, Santos AAC, Miranda RM, Bonelly IS, Neves MSAS, Bersot MI, Santos TP, Gomes MQ, et al. Haemagogus leucocelaenus and Haemagogus janthinomys are the primary vectors in the major yellow fever outbreak in Brazil, 2016-2018. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8:218–231. - PMC - PubMed
Internet Resources
-
- Cyranoski D. New virus identified as likely cause of mystery illness in China. 2020a. [24 April 2020]. Cyranoski D (2020a) New virus identified as likely cause of mystery illness in China, https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-00020-9. - PubMed
-
- Cyranoski D. New virus surging in Asia rattles scientists. 2020b. [24 April 2020]. Cyranoski D (2020b) New virus surging in Asia rattles scientists, https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-00129-x. - PubMed
-
- de Jesus JG, Sacchi C, Claro I, Salles F, Manulli E, da Silva D, de Paiva TM, Pinho M, Afonso AMS, Mathias A, et al. First cases of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Brazil, South America (2 genomes, 3rd March 2020) 2020. [2 May 2020]. (2020) First cases of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Brazil, South America (2 genomes, 3rd March 2020), http://virological.org/t/first-cases-of-coronavirus-disease-covid-19-in-....
-
- Johns Hopkins University COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. 2020. [10 December 2020]. Johns Hopkins University (2020) COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University, https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

