CB1Rs in VMH neurons regulate glucose homeostasis but not body weight
- PMID: 34097543
- PMCID: PMC8321828
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00044.2021
CB1Rs in VMH neurons regulate glucose homeostasis but not body weight
Abstract
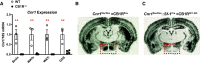
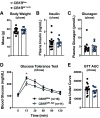
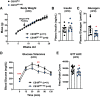
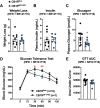
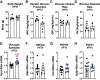
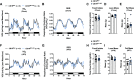
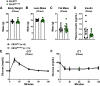
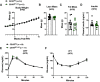
Cannabinoid 1 receptor (CB1R) inverse agonists reduce body weight and improve several parameters of glucose homeostasis. However, these drugs have also been associated with deleterious side effects. CB1R expression is widespread in the brain and in peripheral tissues, but whether specific sites of expression can mediate the beneficial metabolic effects of CB1R drugs, while avoiding the untoward side effects, remains unclear. Evidence suggests inverse agonists may act on key sites within the central nervous system to improve metabolism. The ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) is a critical node regulating energy balance and glucose homeostasis. To determine the contributions of CB1Rs expressed in VMH neurons in regulating metabolic homeostasis, we generated mice lacking CB1Rs in the VMH. We found that the deletion of CB1Rs in the VMH did not affect body weight in chow- and high-fat diet-fed male and female mice. We also found that deletion of CB1Rs in the VMH did not alter weight loss responses induced by the CB1R inverse agonist SR141716. However, we did find that CB1Rs of the VMH regulate parameters of glucose homeostasis independent of body weight in diet-induced obese male mice.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Cannabinoid 1 receptors (CB1Rs) regulate metabolic homeostasis, and CB1R inverse agonists reduce body weight and improve parameters of glucose metabolism. However, the cell populations expressing CB1Rs that regulate metabolic homeostasis remain unclear. CB1Rs are highly expressed in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus (VMH), which is a crucial node that regulates metabolism. With CRISPR/Cas9, we generated mice lacking CB1Rs specifically in VMH neurons and found that CB1Rs in VMH neurons are essential for the regulation of glucose metabolism independent of body weight regulation.
Keywords: CB1R; SR141716; VMH; glucose metabolism; metabolic homeostasis.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

