Human papillomavirus seroprevalence in pregnant women following gender-neutral and girls-only vaccination programs in Finland: A cross-sectional cohort analysis following a cluster randomized trial
- PMID: 34097688
- PMCID: PMC8216524
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003588
Human papillomavirus seroprevalence in pregnant women following gender-neutral and girls-only vaccination programs in Finland: A cross-sectional cohort analysis following a cluster randomized trial
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer elimination through human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination programs requires the attainment of herd effect. Due to its uniquely high basic reproduction number, the vaccination coverage required to achieve herd effect against HPV type 16 exceeds what is attainable in most populations. We have compared how gender-neutral and girls-only vaccination strategies create herd effect against HPV16 under moderate vaccination coverage achieved in a population-based, community-randomized trial.
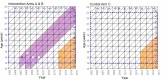
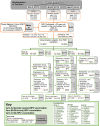
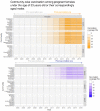
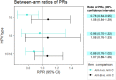
Methods and findings: In 2007-2010, the 1992-1995 birth cohorts of 33 Finnish communities were randomized to receive gender-neutral HPV vaccination (Arm A), girls-only HPV vaccination (Arm B), or no HPV vaccination (Arm C) (11 communities per trial arm). HPV16/18/31/33/35/45 seroprevalence differences between the pre-vaccination era (2005-2010) and post-vaccination era (2011-2016) were compared between all 8,022 unvaccinated women <23 years old and resident in the 33 communities during 2005-2016 (2,657, 2,691, and 2,674 in Arms A, B, and C, respectively). Post- versus pre-vaccination-era HPV seroprevalence ratios (PRs) were compared by arm. Possible outcome misclassification was quantified via probabilistic bias analysis. An HPV16 and HPV18 seroprevalence reduction was observed post-vaccination in the gender-neutral vaccination arm in the entire study population (PR16 = 0.64, 95% CI 0.10-0.85; PR18 = 0.72, 95% CI 0.22-0.96) and for HPV16 also in the herpes simplex virus type 2 seropositive core group (PR16 = 0.64, 95% CI 0.50-0.81). Observed reductions in HPV31/33/35/45 seroprevalence (PR31/33/35/45 = 0.88, 95% CI 0.81-0.97) were replicated in Arm C (PR31/33/35/45 = 0.79, 95% CI 0.69-0.90).
Conclusions: In this study we only observed herd effect against HPV16/18 after gender-neutral vaccination with moderate vaccination coverage. With only moderate vaccination coverage, a gender-neutral vaccination strategy can facilitate the control of even HPV16. Our findings may have limited transportability to other vaccination coverage levels.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov number NCT00534638, https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00534638.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: M.L. has previously received grants from Merck & Co. and GSK Biologicals through his employers the Finnish Institute of Health and Welfare (THL) and the University of Tampere for HPV vaccination studies.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General calls for all countries to take action to help end the suffering caused by cervical cancer. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. [cited 2019 Aug 19]. http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/call-to-action-elimination-cervica....
-
- World Health Organization. Global strategy to accelerate the elimination of cervical cancer as a public health problem. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- Wellcome. Wellcome global monitor 2018 . London: Wellcome; 2019. [cited 2021 May 25]. https://wellcome.org/reports/wellcome-global-monitor/2018.

