DNA damage checkpoint activation affects peptidoglycan synthesis and late divisome components in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 34097787
- PMCID: PMC8600973
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14765
DNA damage checkpoint activation affects peptidoglycan synthesis and late divisome components in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
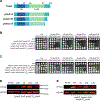
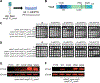
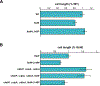
During normal DNA replication, all cells encounter damage to their genetic material. As a result, organisms have developed response pathways that provide time for the cell to complete DNA repair before cell division occurs. In Bacillus subtilis, it is well established that the SOS-induced cell division inhibitor YneA blocks cell division after genotoxic stress; however, it remains unclear how YneA enforces the checkpoint. Here, we identify mutations that disrupt YneA activity and mutations that are refractory to the YneA-induced checkpoint. We find that YneA C-terminal truncation mutants and point mutants in or near the LysM peptidoglycan binding domain render YneA incapable of checkpoint enforcement. In addition, we develop a genetic method which isolated mutations in the ftsW gene that completely bypassed checkpoint enforcement while also finding that YneA interacts with late divisome components FtsL, Pbp2b, and Pbp1. Characterization of an FtsW variant resulted in considerably shorter cells during the DNA damage response indicative of hyperactive initiation of cell division and bypass of the YneA-enforced DNA damage checkpoint. With our results, we present a model where YneA inhibits septal cell wall synthesis by binding peptidoglycan and interfering with interaction between late arriving divisome components causing DNA damage checkpoint activation.
Keywords: DNA damage checkpoint; FtsW; YneA; cell division.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




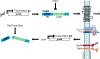
Similar articles
-
DdcA antagonizes a bacterial DNA damage checkpoint.Mol Microbiol. 2019 Jan;111(1):237-253. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14151. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30315724 Free PMC article.
-
YneA, an SOS-induced inhibitor of cell division in Bacillus subtilis, is regulated posttranslationally and requires the transmembrane region for activity.J Bacteriol. 2010 Jun;192(12):3159-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.00027-10. Epub 2010 Apr 16. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20400548 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a dual protease mechanism that promotes DNA damage checkpoint recovery.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jul 6;14(7):e1007512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007512. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29979679 Free PMC article.
-
Class A PBPs: It is time to rethink traditional paradigms.Mol Microbiol. 2021 Jul;116(1):41-52. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14714. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33709487 Review.
-
Regulation of Cell Division in Bacteria by Monitoring Genome Integrity and DNA Replication Status.J Bacteriol. 2020 Jan 2;202(2):e00408-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00408-19. Print 2020 Jan 2. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31548275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MraZ Transcriptionally Controls the Critical Level of FtsL Required for Focusing Z-Rings and Kickstarting Septation in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2022 Sep 20;204(9):e0024322. doi: 10.1128/jb.00243-22. Epub 2022 Aug 9. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35943250 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the LexA-Mediated DNA Damage Response in Streptomyces venezuelae.J Bacteriol. 2022 Aug 16;204(8):e0010822. doi: 10.1128/jb.00108-22. Epub 2022 Jul 13. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35862789 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and kinase activity of bacterial cell cycle regulator CcrZ.PLoS Genet. 2022 May 16;18(5):e1010196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010196. eCollection 2022 May. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35576203 Free PMC article.
-
Transient inhibition of cell division in competent pneumococcal cells results from deceleration of the septal peptidoglycan complex.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5666. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60600-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40595580 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial developmental checkpoint that directly monitors cell surface morphogenesis.Dev Cell. 2022 Feb 7;57(3):344-360.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.12.021. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Dev Cell. 2022. PMID: 35065768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- [Dataset], Hawkins WD, Burby PE and Simmons LA (2021). “Whole-genome sequencing coverage for identification of ftsW mutations.” SRA BioProject.
-
- Au N, Kuester-Schoeck E, Mandava V, Bothwell LE, Canny SP, Chachu K, Colavito SA, Fuller SN, Groban ES, Hensley LA, O’Brien TC, Shah A, Tierney JT, Tomm LL, O’Gara TM, Goranov AI, Grossman AD and Lovett CM (2005). “Genetic composition of the Bacillus subtilis SOS system.” J Bacteriol 187(22): 7655–7666. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhambhani A, Iadicicco I, Lee J, Ahmed S, Belfatto M, Held D, Marconi A, Parks A, Stewart CR, Margolin W, Levin PA and Haeusser DP (2020). “Bacteriophage SP01 Gene Product 56 Inhibits Bacillus subtilis Cell Division by Interacting with FtsL and Disrupting Pbp2B and FtsW Recruitment.” J Bacteriol 203(2):e00463–20.doi: 10.1128/JB.00463-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bojer MS, Frees D and Ingmer H (2020). “SosA in Staphylococci: an addition to the paradigm of membrane-localized, SOS-induced cell division inhibition in bacteria.” Curr Genet 66(3): 495–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

