KTE-X19 for relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: phase 2 results of the single-arm, open-label, multicentre ZUMA-3 study
- PMID: 34097852
- PMCID: PMC11613962
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01222-8
KTE-X19 for relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: phase 2 results of the single-arm, open-label, multicentre ZUMA-3 study
Abstract
Background: Despite treatment with novel therapies and allogeneic stem-cell transplant (allo-SCT) consolidation, outcomes in adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia remain poor, underlining the need for more effective therapies.
Methods: We report the pivotal phase 2 results of ZUMA-3, an international, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study evaluating the efficacy and safety of the autologous anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy KTE-X19 in adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Patients were enrolled at 25 sites in the USA, Canada, and Europe. Eligible patients were aged 18 years or older, with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-1, and morphological disease in the bone marrow (>5% blasts). After leukapheresis and conditioning chemotherapy, patients received a single KTE-X19 infusion (1 × 106 CAR T cells per kg bodyweight). The primary endpoint was the rate of overall complete remission or complete remission with incomplete haematological recovery by central assessment. Duration of remission and relapse-free survival, overall survival, minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity rate, and allo-SCT rate were assessed as secondary endpoints. Efficacy and safety analyses were done in the treated population (all patients who received a dose of KTE-X19). This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02614066.
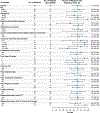
Findings: Between Oct 1, 2018, and Oct 9, 2019, 71 patients were enrolled and underwent leukapheresis. KTE-X19 was successfully manufactured for 65 (92%) patients and administered to 55 (77%). The median age of treated patients was 40 years (IQR 28-52). At the median follow-up of 16·4 months (13·8-19·6), 39 patients (71%; 95% CI 57-82, p<0·0001) had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete haematological recovery, with 31 (56%) patients reaching complete remission. Median duration of remission was 12·8 months (95% CI 8·7-not estimable), median relapse-free survival was 11·6 months (2·7-15·5), and median overall survival was 18·2 months (15·9-not estimable). Among responders, the median overall survival was not reached, and 38 (97%) patients had MRD negativity. Ten (18%) patients received allo-SCT consolidation after KTE-X19 infusion. The most common adverse events of grade 3 or higher were anaemia (27 [49%] patients) and pyrexia (20 [36%] patients). 14 (25%) patients had infections of grade 3 or higher. Two grade 5 KTE-X19-related events occurred (brain herniation and septic shock). Cytokine release syndrome of grade 3 or higher occurred in 13 (24%) patients and neurological events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 14 (25%) patients.
Interpretation: KTE-X19 showed a high rate of complete remission or complete remission with incomplete haematological recovery in adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, with the median overall survival not reached in responding patients, and a manageable safety profile. These findings indicate that KTE-X19 has the potential to confer long-term clinical benefit to these patients.
Funding: Kite, a Gilead Company.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests BDS reports honoraria from Kite, a Gilead Company, and BeiGene; a consultancy or advisory role for BeiGene, Pepromene Bio, Kite, a Gilead Company, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Juno, Novartis, Pfizer, Amgen, Precision Biosciences, Adaptive Biotechnologies, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals; research funding from Kite, a Gilead Company, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Chotiner Pediatric Research Foundation, Lymphoma Research Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health; travel support from Kite, a Gilead Company; a leadership or fiduciary role for the National Cancer Center Network, the International Working Group for Acute Leukemia and CAR T, and the Society of Hematologic Oncology; and payment for expert testimony from Bayer. AG reports consultancy or advisory role for Amgen, Kite, a Gilead Company, Atara, Wugen, and Celgene; and research funding from Amgen and Kite, a Gilead Company. OOO reports a consultancy or advisory role for Kite, a Gilead Company, Pfizer, and Janssen; and research funding from Kite, a Gilead Company. ACL reports honoraria from Amgen; a consultancy or advisory role for Amgen, Pfizer, BMS, and Incyte; and research funding from Autolus, Amphivena, Astellas, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Kadmon, Kite, a Gilead Company, and Pharmacyclics. NB reports honoraria from Servier and Jazz Pharmaceuticals; a consultancy or advisory role for Amgen, Pfizer, Gilead Sciences, Novartis, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Servier; and travel support from Amgen. RDC reports employment with Seagen; stock or other ownership in Seagen; honoraria from Pfizer; a consultancy or advisory role for Kite, a Gilead Company, Pfizer, Amgen, and Pepromene Bio; research funding from Pfizer, Merck, Amgen, Kite, a Gilead Company, and Vanda; and travel support from Pfizer. MRBi reports honoraria from Kite, a Gilead Company; a consultancy or advisory role for Kite, a Gilead Company; and speakers' bureau participation for Kite, a Gilead Company. MST reports consultancy or advisory role for Gilead Sciences, Roche, and Regeneron; and research funding from Amgen, Kite, a Gilead Company, Roche, MacroGenics, and Regeneron. DT reports a consultancy or advisory role for Takeda and Kite, a Gilead Company; speakers' bureau participation for Takeda and Kite, a Gilead Company; and research funding from BMS. KMO reports a consultancy or advisory role for Beam Therapeutics. MLA reports a consultancy or advisory role for Gilead Sciences, Kite, a Gilead Company, and Syndax Pharmaceuticals. YL reports a consultancy or advisory role for Kite, a Gilead Company, Celgene, Juno, Bluebird Bio, Janssen, Legend, Gamida Cell, Novartis, Iovance, Takeda, Fosun Kite, and Sorrento; and research funding from Kite, a Gilead Company, Celgene, Bluebird Bio, Janssen, Legend, Merck, Takeda, and Boston Scientific. GJS reports honoraria from Kite, a Gilead Company. JHP reports honoraria from Clinical Care Options and Aptitude Health; a consultancy or advisory role for Kite, a Gilead Company, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Autolus, Allogene, Artiva, Baxalta, Curocell, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Innate Pharma, Intellia, Kura Oncology, Minerva, Pfizer, Takeda, Umoja, Affyimmune, and Bright Pharmaceutical Services. MA reports consultancy or advisory role for Celgene; speakers' bureau participation for BMS and Kite, a Gilead Company; and research funding from the National Institutes of Health and California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. MCM reports honoraria from Gilead Sciences, Janssen-Cilag, BMS, Roche, and Celgene; a consultancy or advisory role for Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, and Alnylam; travel support from Celgene; and a leadership or fiduciary role for diagnostic guidelines for plasma cell dyscrasias and treatment guidelines for amyloid light-chain amyloidosis in the Netherlands. DJD reports honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Agios, Autolus, Blueprint Medicines, Forty Seven, GlycoMimetics, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Pfizer, Servier, and Takeda; a consultancy or advisory role for Daiichi-Sankya, FibroGen, and Mount Sinai Hospital; research funding from AbbVie, GlycoMimetics, Novartis, and Blueprint Medicines; and travel support from GlycoMimetics. PS reports research funding from Kite, a Gilead Company. DJ reports research funding from Pfizer and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. CF and JMR report employment with Kite, a Gilead Company; and stock or other ownership in Gilead Sciences. JD reports employment with Kite, a Gilead Company; and stock or other ownership in Kite, a Gilead Company. TS reports employment with Kite, a Gilead Company; stock or other ownership in Kite, a Gilead Company; research funding from Kite, a Gilead Company; and travel support from Kite, a Gilead Company. FM reports employment with Kite, a Gilead Company; stock or other ownership in Gilead Sciences; and travel support from Kite, a Gilead Company. RV reports employment with Kite, a Gilead Company. BKM reports employment with Kite, a Gilead Company; and stock or other ownership in Kite, a Gilead Company, GlaxoSmithKline, Immatics, Novartis, BMS, and Roche. RH reports consultancy or advisory role for Kite, a Gilead Company; research funding from Kite, a Gilead Company; and travel support from Kite, a Gilead Company. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

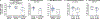
Comment in
-
CD19 CAR T cells for adults with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.Lancet. 2021 Aug 7;398(10299):466-467. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01289-7. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 34097851 No abstract available.
-
KTE-X19 efficacious in adults with B-ALL.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021 Aug;18(8):470. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00537-6. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34155393 No abstract available.
References
-
- Paul S, Kantarjian H, Jabbour EJ. Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mayo Clin Proc 2016; 91(11): 1645–66. - PubMed
-
- Topp MS, Gokbuget N, Stein AS, et al. Safety and activity of blinatumomab for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16(1): 57–66. - PubMed

