Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat substrains show differences in model traits for addiction risk and cocaine self-administration: Implications for a novel rat reduced complexity cross
- PMID: 34097899
- PMCID: PMC8265396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113406
Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat substrains show differences in model traits for addiction risk and cocaine self-administration: Implications for a novel rat reduced complexity cross
Abstract
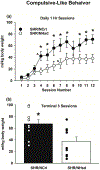
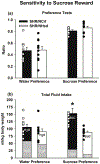
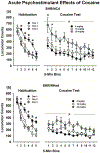
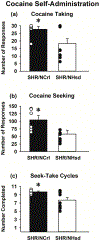
Forward genetic mapping of F2 crosses between closely related substrains of inbred rodents - referred to as a reduced complexity cross (RCC) - is a relatively new strategy for accelerating the pace of gene discovery for complex traits, such as drug addiction. RCCs to date were generated in mice, but rats are thought to be optimal for addiction genetic studies. Based on past literature, one inbred Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat substrain, SHR/NCrl, is predicted to exhibit a distinct behavioral profile as it relates to cocaine self-administration traits relative to another substrain, SHR/NHsd. Direct substrain comparisons are a necessary first step before implementing an RCC. We evaluated model traits for cocaine addiction risk and cocaine self-administration behaviors using a longitudinal within-subjects design. Impulsive-like and compulsive-like traits were greater in SHR/NCrl than SHR/NHsd, as were reactivity to sucrose reward, sensitivity to acute psychostimulant effects of cocaine, and cocaine use studied under fixed-ratio and tandem schedules of cocaine self-administration. Compulsive-like behavior correlated with the acute psychostimulant effects of cocaine, which in turn correlated with cocaine taking under the tandem schedule. Compulsive-like behavior also was the best predictor of cocaine seeking responses. Heritability estimates indicated that 22 %-40 % of the variances for the above phenotypes can be explained by additive genetic factors, providing sufficient genetic variance to conduct genetic mapping in F2 crosses of SHR/NCrl and SHR/NHsd. These results provide compelling support for using an RCC approach in SHR substrains to uncover candidate genes and variants that are of relevance to cocaine use disorders.
Keywords: Addiction vulnerability traits; Cocaine; SHR/NCrl substrain; SHR/NHsd substrain.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of preexisting inhibitory control deficits vs. drug use history in mediating insensitivity to aversive consequences in a rat model of polysubstance use.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Aug;239(8):2377-2394. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06134-4. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35391547 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and genetic evidence for a novel animal model of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Predominantly Inattentive Subtype.Behav Brain Funct. 2008 Dec 1;4:56. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-4-56. Behav Brain Funct. 2008. PMID: 19046438 Free PMC article.
-
Autism-related behavioral phenotypes in an inbred rat substrain.Behav Brain Res. 2014 Aug 1;269:103-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.04.035. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Behav Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24780868 Free PMC article.
-
The spontaneously hypertensive rat model of ADHD--the importance of selecting the appropriate reference strain.Neuropharmacology. 2009 Dec;57(7-8):619-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19698722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Responses to novelty and vulnerability to cocaine addiction: contribution of a multi-symptomatic animal model.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Nov 1;2(11):a011940. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a011940. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 23125204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the Risk Genes Associated With Vulnerability to Addiction: Major Findings From Transgenic Animals.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jan 12;15:811192. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.811192. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35095405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex and heredity are determinants of drug intake in a novel model of rat oral oxycodone self-administration.Genes Brain Behav. 2021 Nov;20(8):e12770. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12770. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Genes Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 34459088 Free PMC article.
-
Role of preexisting inhibitory control deficits vs. drug use history in mediating insensitivity to aversive consequences in a rat model of polysubstance use.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Aug;239(8):2377-2394. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06134-4. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35391547 Free PMC article.
-
The relative reinforcing efficacy of nicotine in an adolescent rat model of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2023 May 15;14:1154773. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1154773. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37255676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2019, https://www.samhsa.gov/data/release/2019-national-survey-drug-use-and-he...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

