Nanobodies from camelid mice and llamas neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants
- PMID: 34098567
- PMCID: PMC8260353
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03676-z
Nanobodies from camelid mice and llamas neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants
Abstract
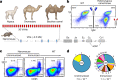
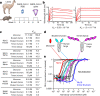
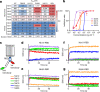
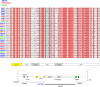
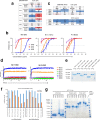
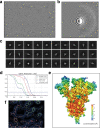
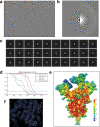
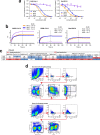
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, SARS-CoV-2 has caused millions of deaths worldwide. Although a number of vaccines have been deployed, the continual evolution of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the virus has challenged their efficacy. In particular, the emerging variants B.1.1.7, B.1.351 and P.1 (first detected in the UK, South Africa and Brazil, respectively) have compromised the efficacy of sera from patients who have recovered from COVID-19 and immunotherapies that have received emergency use authorization1-3. One potential alternative to avert viral escape is the use of camelid VHHs (variable heavy chain domains of heavy chain antibody (also known as nanobodies)), which can recognize epitopes that are often inaccessible to conventional antibodies4. Here, we isolate anti-RBD nanobodies from llamas and from mice that we engineered to produce VHHs cloned from alpacas, dromedaries and Bactrian camels. We identified two groups of highly neutralizing nanobodies. Group 1 circumvents antigenic drift by recognizing an RBD region that is highly conserved in coronaviruses but rarely targeted by human antibodies. Group 2 is almost exclusively focused to the RBD-ACE2 interface and does not neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants that carry E484K or N501Y substitutions. However, nanobodies in group 2 retain full neutralization activity against these variants when expressed as homotrimers, and-to our knowledge-rival the most potent antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 that have been produced to date. These findings suggest that multivalent nanobodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 mutations through two separate mechanisms: enhanced avidity for the ACE2-binding domain and recognition of conserved epitopes that are largely inaccessible to human antibodies. Therefore, although new SARS-CoV-2 mutants will continue to emerge, nanobodies represent promising tools to prevent COVID-19 mortality when vaccines are compromised.
Conflict of interest statement
The National Institutes of Health has filed a provisional patent application in connection with this work on which J.X. and R.C. are inventors (US patent 63-151,530).
Figures

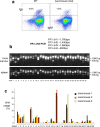
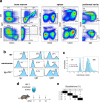
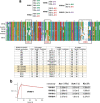
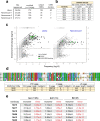

Update of
-
Multimeric nanobodies from camelid engineered mice and llamas potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Mar 4:2021.03.04.433768. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.04.433768. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: Nature. 2021 Jul;595(7866):278-282. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03676-z. PMID: 33688659 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Engineered single-domain antibodies tackle COVID variants.Nature. 2021 Jul;595(7866):176-178. doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-01721-5. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34193999 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wu, K. et al. mRNA-1273 vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies against spike mutants from global SARS-CoV-2 variants. Preprint at 10.1101/2021.01.25.427948 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

