Coordinated action of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins on competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network members in primary human keratinocytes
- PMID: 34098875
- PMCID: PMC8185923
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08361-y
Coordinated action of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins on competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network members in primary human keratinocytes
Abstract
Background: miRNAs and lncRNAs can regulate cellular biological processes both under physiological and pathological conditions including tumour initiation and progression. Interactions between differentially expressed diverse RNA species, as a part of a complex intracellular regulatory network (ceRNA network), may contribute also to the pathogenesis of HPV-associated cancer. The purpose of this study was to investigate the global expression changes of miRNAs, lncRNAs and mRNAs driven by the E6 and E7 oncoproteins of HPV16, and construct a corresponding ceRNA regulatory network of coding and non-coding genes to suggest a regulatory network associated with high-risk HPV16 infections. Furthermore, additional GO and KEGG analyses were performed to understand the consequences of mRNA expression alterations on biological processes.
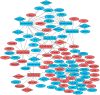
Methods: Small and large RNA deep sequencing were performed to detect expression changes of miRNAs, lncRNAs and mRNAs in primary human keratinocytes expressing HPV16 E6, E7 or both oncoproteins. The relationships between lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs were predicted by using StarBase v2.0, DianaTools-LncBase v.2 and miRTarBase. The lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network was visualized with Cytoscape v3.4.0. GO and KEEG pathway enrichment analysis was performed using DAVID v6.8.
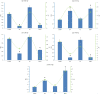
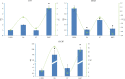
Results: We revealed that 85 miRNAs in 21 genomic clusters and 41 lncRNAs were abnormally expressed in HPV E6/E7 expressing cells compared with controls. We constructed a ceRNA network with members of 15 lncRNAs - 43 miRNAs - 358 mRNAs with significantly altered expressions. GO and KEGG functional enrichment analyses identified numerous cancer related genes, furthermore we recognized common miRNAs as key regulatory elements in biological pathways associated with tumorigenesis driven by HPV16.
Conclusions: The multiple molecular changes driven by E6 and E7 oncoproteins resulting in the malignant transformation of HPV16 host cells occur, at least in part, due to the abnormal alteration in expression and function of non-coding RNA molecules through their intracellular competing network.
Keywords: Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA); E6; E7; HPV16; Long non-coding RNA; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Modulation of microRNA-mRNA Target Pairs by Human Papillomavirus 16 Oncoproteins.mBio. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):e02170-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02170-16. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28049151 Free PMC article.
-
Human Papillomavirus E6/E7 and Long Noncoding RNA TMPOP2 Mutually Upregulated Gene Expression in Cervical Cancer Cells.J Virol. 2019 Apr 3;93(8):e01808-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01808-18. Print 2019 Apr 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30728257 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNAs dysregulated in human foreskin keratinocytes (HFKs) expressing the human papillomavirus (HPV) Type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins.Microrna. 2013;2(1):2-13. doi: 10.2174/2211536611302010002. Microrna. 2013. PMID: 25070710
-
High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Oncogenic E6/E7 mRNAs Splicing Regulation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 27;12:929666. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.929666. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35832386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction between human papilloma viruses related cancers and non-coding RNAs.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Jun;234:153939. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153939. Epub 2022 May 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35561523 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-627-5p inhibits malignant progression of cervical cancer by targeting ANGPTL4.Eur J Histochem. 2025 Apr 7;69(2):4161. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2025.4161. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Eur J Histochem. 2025. PMID: 40191921 Free PMC article.
-
HPV16 E6 promoting cervical cancer progression through down-regulation of miR-320a to increase TOP2A expression.Cancer Med. 2024 Feb;13(3):e6875. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6875. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38205938 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Modifications and Novel Protein-Binding Sites in Pre-miR-675-Explaining Its Regulatory Mechanism in Carcinogenesis.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Aug 10;9(4):45. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9040045. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37624037 Free PMC article.
-
The Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressive Long Non-Coding RNA-microRNA-Messenger RNA Regulatory Axes Identified by Analyzing Multiple Platform Omics Data from Cr(VI)-Transformed Cells and Their Implications in Lung Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 20;10(10):2334. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102334. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289596 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and identification analysis of core markers for leukemia and cervical cancer: Calmodulin 3 as a core target.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Apr 4;104(14):e41665. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041665. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40193646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses and cancer: from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2(5):342–350, DOI: 10.1038/nrc798. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

