Outcomes with multi-disciplinary management of central lung tumors with CT-guided percutaneous high dose rate brachyablation
- PMID: 34098977
- PMCID: PMC8186067
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-021-01826-1
Outcomes with multi-disciplinary management of central lung tumors with CT-guided percutaneous high dose rate brachyablation
Abstract
Background: Centrally located lung tumors present treatment challenges given their proximity to mediastinal structures including the central airway, esophagus, major vessels, and heart. Therapeutic options can be limited for medically inoperable patients, particularly if they have received previous thoracic radiotherapy. High dose rate (HDR) brachyablation was developed to improve the therapeutic ratio for patients with central lung tumors. The purpose of this study is to report initial safety and efficacy outcomes with this treatment for central lung malignancies.
Methods: From September 2015 to August 2019, a total of 25 patients with 37 pulmonary tumors were treated with percutaneous HDR brachyablation. Treatment was delivered by a multi-disciplinary team of interventional radiologists, pulmonologists, and radiation oncologists. Twenty-three patients received a median dose of 21.5 Gy (range 15-27.5) in a single fraction, whereas two patients received median dose of 24.75 Gy (range 24-25.5) over 2-3 fractions. Tumor local control (LC) was evaluated by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1. Treatment-related toxicities were graded by Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v5.0, with adverse events less than 90 days defined as acute, and those occurring later were defined as late. LC, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) rates were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method.
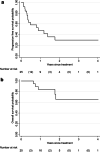
Results: Of 37 treated tumors, 88% were metastatic. Tumor location was central and ultra-central in 24.3% and 54.1%, respectively. Average tumor volume was 11.6 cm3 (SD 12.4, range 0.57-62.8). Median follow-up was 19 months (range 3-48). Two-year LC, PFS, and OS were 96.2%, 29.7%, and 65.5%, respectively. Thirteen of 39 (33.3%) catheter implantation procedures were associated with trace minor pneumothorax requiring no intervention, 1 (2.5%) procedure with minor radiographic pulmonary hemorrhage, and 4 (10.3%) with major pneumothorax requiring chest tube insertions. All procedural complications resolved within 24 h from treatment. Acute grade 1-2 toxicity was identified in 4 patients, whereas none developed late toxicity beyond 90 days of follow-up.
Conclusion: Percutaneous HDR brachyablation is a safe and promising treatment option for centrally located primary and metastatic lung tumors. Future comparisons with stereotactic body radiotherapy and other ablative techniques are warranted to expand multi-disciplinary management options.
Keywords: Brachyablation; Brachytherapy; High-dose-rate brachytherapy; Interstitial brachytherapy; Pulmonary metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computed Tomography-Guided Interstitial High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy in Combination With Regional Positive Lymph Node Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy in Locally Advanced Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 1 Clinical Trial.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015 Aug 1;92(5):1027-1034. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.04.019. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015. PMID: 26194678 Clinical Trial.
-
Interstitial single fraction brachytherapy for malignant pulmonary tumours.Strahlenther Onkol. 2021 May;197(5):416-422. doi: 10.1007/s00066-021-01758-5. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021. PMID: 33725134
-
Tumor Control and Toxicity after SBRT for Ultracentral, Central, and Paramediastinal Lung Tumors.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2019 Mar;9(2):e196-e202. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30496842 Free PMC article.
-
Innovations in modern low-LET radiotherapy regimens for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis and systematic review of high-dose-rate brachytherapy, stereotactic body radiotherapy, and hypofractionated proton therapy.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 26;25(1):942. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14328-0. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40420058 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography guided interstitial percutaneous high-dose-rate brachytherapy in the management of lung malignancies. A review of the literature.Brachytherapy. 2021 Jul-Aug;20(4):892-899. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2021.03.012. Epub 2021 May 10. Brachytherapy. 2021. PMID: 33985903 Review.
Cited by
-
Salvage percutaneous high-dose-rate brachyablation after stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2024 Apr;16(2):150-155. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2024.139103. Epub 2024 Apr 23. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2024. PMID: 38808204 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchial artery chemoembolization in the treatment of refractory central lung cancer with atelectasis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 12;14:1343324. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1343324. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38933450 Free PMC article.
-
Single-fraction high-dose-rate brachytherapy: a scoping review on outcomes and toxicities for all disease sites.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2022 Oct;14(5):481-494. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2022.121477. Epub 2022 Nov 25. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2022. PMID: 36478697 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in radioactive seed implantation brachytherapy of non-small cell lung cancer: a narrative review.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Mar 29;16(3):2167-2176. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1600. Epub 2024 Mar 25. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38617768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interstitial High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Combined with External Beam Radiation Therapy for Dose Escalation in the Primary Treatment of Locally Advanced, Non-Resectable Superior Sulcus (Pancoast) Tumors: Results of a Monocentric Retrospective Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 11;13(24):7550. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247550. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39768473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bi N, Shedden K, Zheng X, Kong F. Comparison of the effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation with stereotactic body radiation therapy in inoperable stage i non-small cell lung cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2013;3(2 Suppl 1):S19. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2013.01.066. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Sidiqi BU, Yorke ED, McKnight D, Dick-Godfrey R, Torres D, et al. Toxicity and local control in "ultra-central" lung tumors treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;102(3):S10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.06.118. - DOI

