Cannabinoid receptors distribution in mouse cortical plasma membrane compartments
- PMID: 34099009
- PMCID: PMC8183067
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-021-00801-x
Cannabinoid receptors distribution in mouse cortical plasma membrane compartments
Abstract
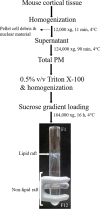
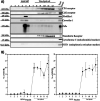
The type 1 and type 2 cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2 receptors) are class A G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that are activated by endogenous lipids called endocannabinoids to modulate neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission in neurons throughout the central nervous system (CNS), and inflammatory processes throughout the body. CB1 receptor is one of the most abundant GPCRs in the CNS and is involved in many physiological and pathophysiological processes, including mood, appetite, and nociception. CB2 receptor is primarily found on immunomodulatory cells of both the CNS and the peripheral immune system. In this study, we isolated lipid raft and non-lipid raft fractions of plasma membrane (PM) from mouse cortical tissue by using cold non-ionic detergent and sucrose gradient centrifugation to study the localization of CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor. Lipid raft and non-lipid raft fractions were confirmed by flotillin-1, caveolin-1 and transferrin receptor as their protein biomarkers. Both CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor were found in non-raft compartments that is inconsistent with previous findings in cultured cell lines. This study demonstrates compartmentalization of both CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor in cortical tissue and warrants further investigation of CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor compartmental distribution in various brain regions and cell types.
Keywords: Lipid rafts; Type 1 cannabinoid receptor; Type 2 cannabinoid receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jahan P. Marcu JBS. Molecular pharmacology of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. In: Preedy VR, editor. Neuropathology of drug addictions and substance misuse. Academic Press; 2016. p. 713-721.
-
- Kuner GM. Anatomical distribution of receptors, ligands and enzymes in the brain and in the spinal cord: circuitries and neurochemistry. In: Köfalvi A, editor. Cannabinoids and the brain. Boston: Springer US; 2008. pp. 161–201.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

